Figure 1. Disorders Associated with Mutations of JAKs and STATs.
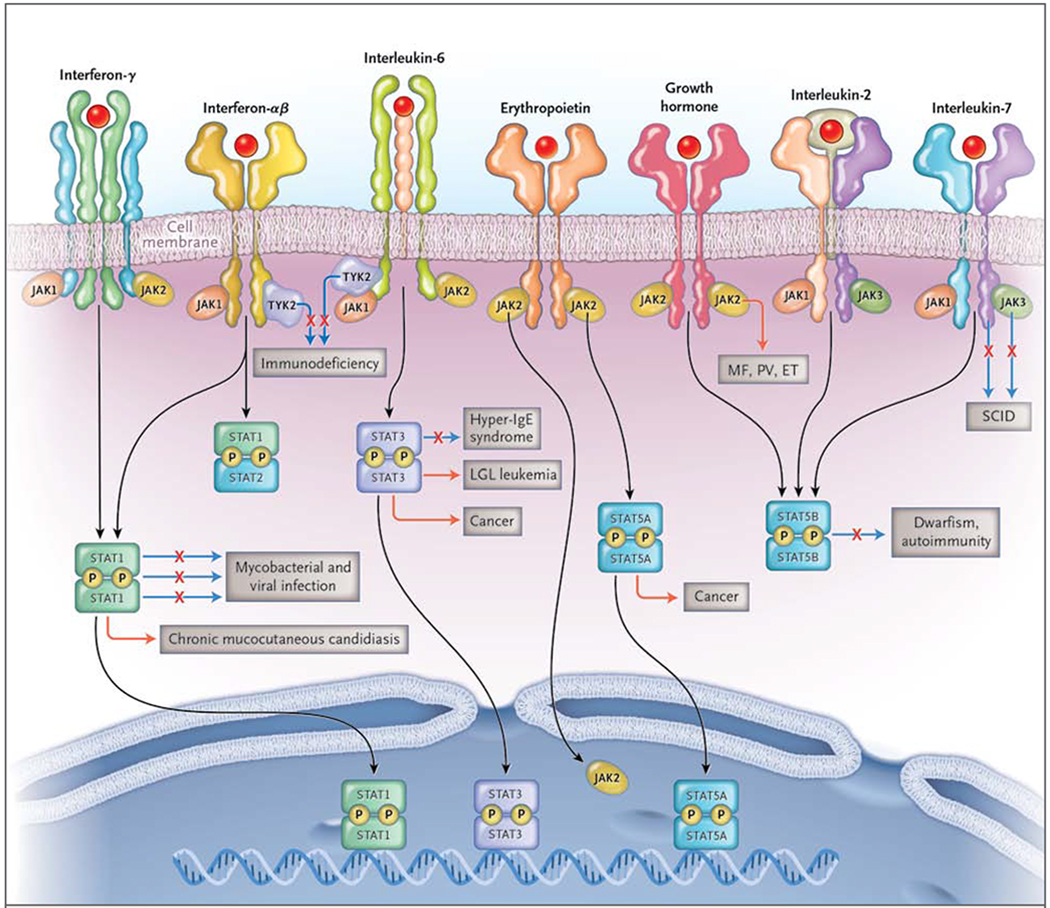
A major subset of cytokines includes those that signal through Janus kinases (JAKs) and signal transducers and activators (STATs). These cytokines include (but are not limited to) interferons, such as interferon-γ, interferon-α, and interferon-β; interleukin-6; erythropoietin; growth hormone; interleukin-2; and interleukin-7. There are four JAKs: JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2). Activated JAKs phosphorylate (P) and activate STATs and other pathways. Some JAKs are associated with many different cytokine receptors, but JAK3 associates with only one subunit, the common interleukin-2Rγ chain, or γc. Loss-of-function mutations (denoted by a solid line, with an X) of the genes encoding γc and JAK3 result in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). Mutation of TYK2 also results in immunodeficiency. Gain-of-function JAK2 mutations (denoted by an orange line) underlie polycythemia vera (PV), essential thrombocytosis (ET), and myelofibrosis (MF). Constitutive activation and mutation of JAKs is also associated with a variety of cancers. Activated JAKs, in turn, activate STATs and other pathways. Activated STATs translocate to the nucleus, bind DNA, and regulate gene expression. Mutations of STAT1 result in several distinct disorders. Autosomal dominant loss-of-function mutations result in susceptibility to mycobacteria only. Autosomal recessive mutations cause susceptibility to mycobacteria and viruses. In contrast, autosomal dominant gain-of-function mutations cause chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis, other infections, and aneurysms. Loss-of-function mutations of STAT3 result in the hyper-IgE syndrome. Mutations in STAT3 also cause large granular lymphocytic (LGL) leukemia. Constitutive STAT3 and STAT5 activation (an orange line) is associated with many cancers. Mutations of STAT5B result in a syndrome characterized by dwarfism and autoimmunity. In addition to their effect on STATs, JAKs can have direct nuclear effects by phosphorylating histones.
