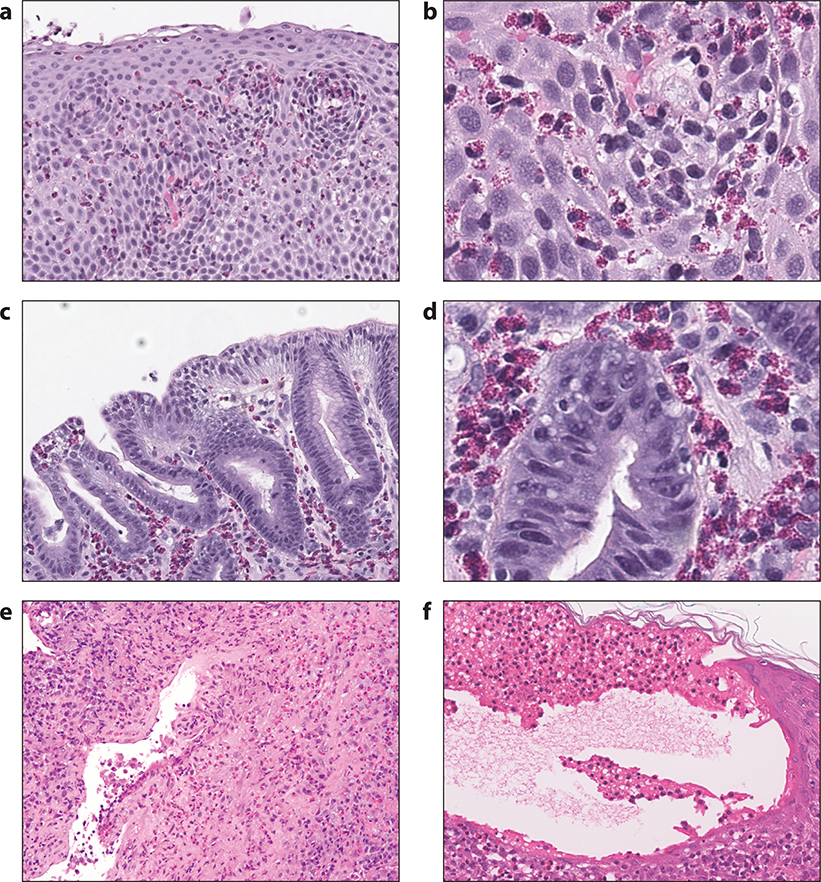
Figure 7.
Histologic findings in EGID, EGPA and bullous pemphigoid. Panels a and b: hematoxylin and eosin stained section of a biopsy from a patient with eosinophilic esophagitis, at both lower and higher power magnification, showing increased intraepithelial eosinophils, epithelial spongiosis and basal cell hyperplasia; Panels c and d: hematoxylin and eosin stained section of a biopsy from a patient with eosinophilic gastritis, at both lower and higher power magnification, showing increased eosinophils in the gastric lamina propria; Panel e: hematoxylin and eosin stained section of a lung biopsy from a patient with EGPA showing a dense interstitial infiltrate rich in eosinophils, lymphocytes and plasma cells involving a vessel wall with focal fibrinous changes; Panel f: hematoxylin and eosin stained section of a skin biopsy from a patient with bullous pemphigoid showing a sub-epidermal blister with numerous eosinophils aligned along the cutaneous basement membrane zone. Also present is significant epidermal edema (spongiosis) with a few intraepithelial eosinophils.