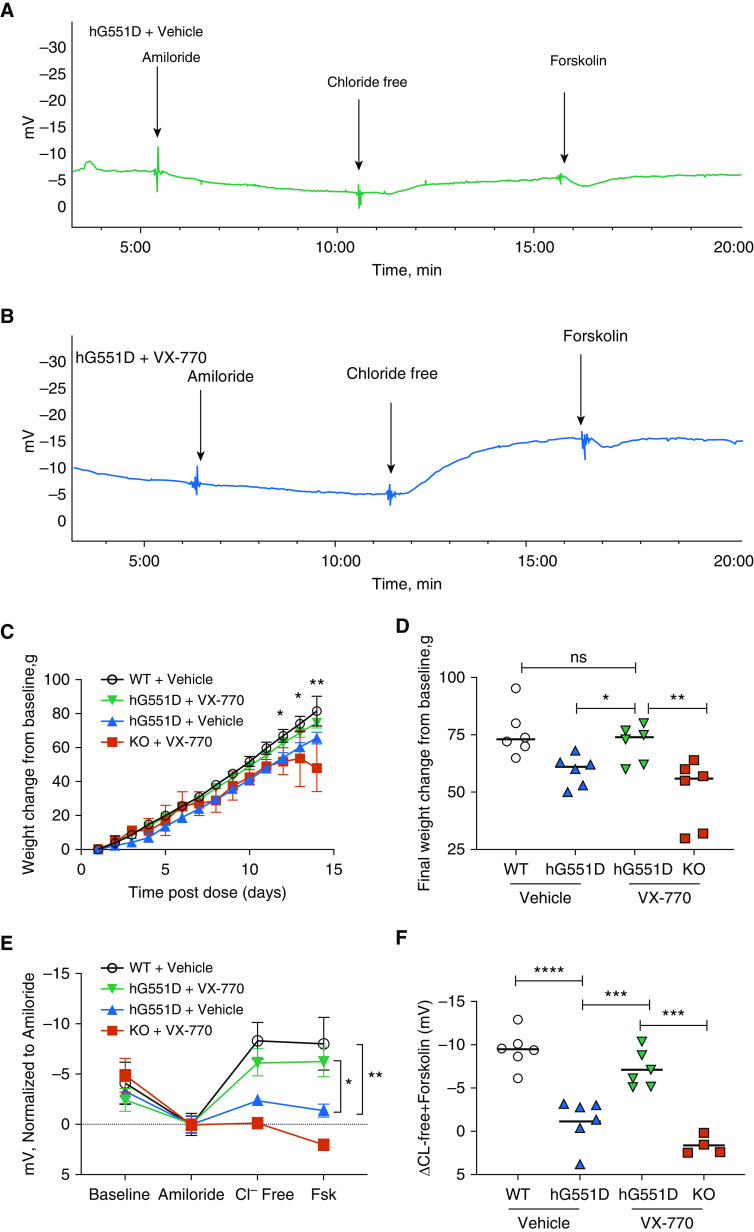
Figure 4.
The hG551D rat responds to in vivo treatment with VX-770. VX-770 was dosed by oral gavage to hG551D and knockout rats for 14 days, beginning at weaning, and nasal potential difference was measured. Representative tracings of (A) hG551D + vehicle and (B) hG551D + VX-770 are depicted. (C) Weights of these groups, compared with untreated hG551D and wild-type (WT) rats, indicate increased weight in the last few days of therapy for hG551D + VX-770 rats compared with untreated hG551D rats. (D) The final weight change per group indicates that hG551D rats were able to gain as much weight as WT rats after 14 days of treatment. (E) Summary data of nasal potential difference measurements of WT, hG551D, hG551D + VX-770, and knockout + VX-770 rats at baseline and after amiloride, with Cl− free and Cl− free + 20 μM forskolin. (F) Untreated hG551D rats had a smaller change in potential difference after the Cl− free + forskolin addition compared with WT rats; this was increased in hG551D rats + VX-770. ns = P > 0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. n = 4–6/condition. FSK = forskolin; KO = knockout.