Figure 1.
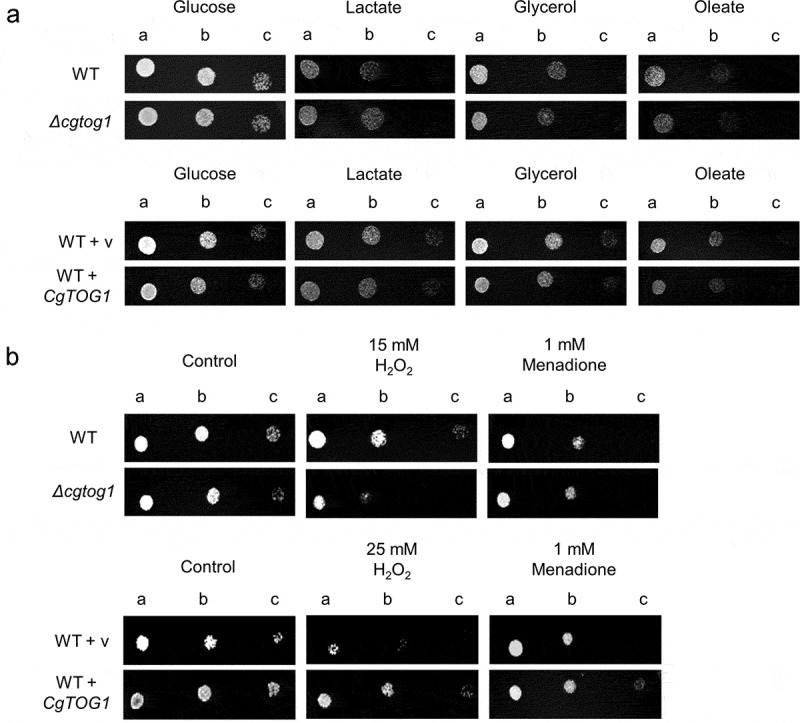
CgTOG1 confers resistance to oxidative stress inducers but is not required for the utilization of alternative carbon sources. (a) Comparison of spot growth assays of the KUE100 C. glabrata wild type and derived Δcgtog1 deletion mutant, as well as the L5U1 C. glabrata wild type strain, harboring the pGREG576 cloning vector, or the pGREG576_MTI_CgTOG1 expression plasmid, in the presence of glucose, lactate, glycerol or oleate as carbon sources. (b) Comparison of spot growth assays of the KUE100 C. glabrata wild type and derived Δcgtog1 deletion mutant, as well as the L5U1 C. glabrata wild type strain, harboring the pGREG576 cloning vector, or the pGREG576_MTI_CgTOG1 expression plasmid, in the presence of oxidative stress inducers H2O2 and menadione. (c) Comparison of spot growth assays of the KUE100 C. glabrata wild type and derived Δcgtog1 deletion mutant, as well as the L5U1 C. glabrata wild type strain, harboring the pGREG576 cloning vector, or the pGREG576_MTI_CgTOG1 expression plasmid, in the presence of distinct carbon sources and the oxidative stress inducer H2O2. (d) Comparison of spot growth assays of the KUE100::URA- C. glabrata wild type strain and the derived KUE100_Δcgtog1:URA- deletion mutant, harboring the pGREG576 cloning vector, or the pGREG576_MTI_CgTOG1 expression plasmid, in the presence of the oxidative stress inducer H2O2. The inocula were prepared as described in the materials and methods section. Cell suspensions used to prepare the spots were 1:5 (b) and 1:25 (c) dilutions of the cell suspension used in (a). The displayed images are representative of at least three independent experiments
