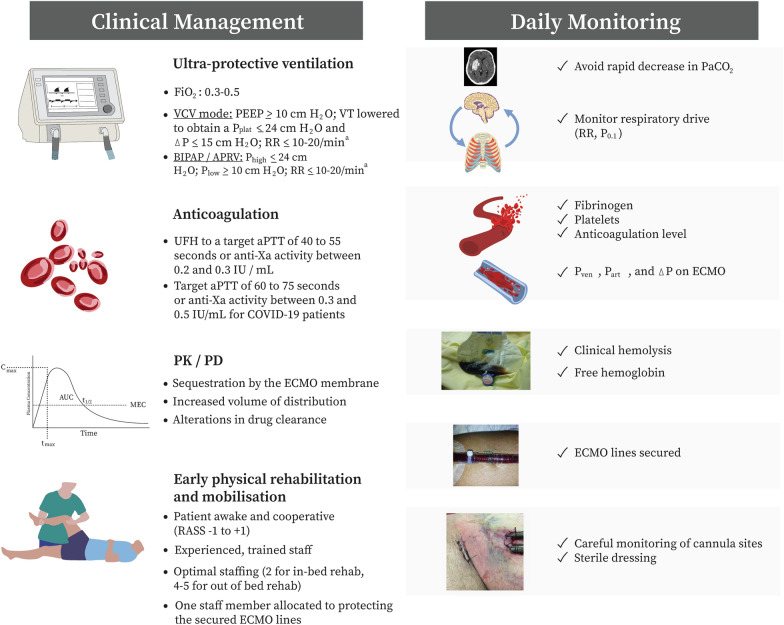
Fig. 3.
Clinical management and daily monitoring of ECMO for ARDS. VV-ECMO venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, VCV volume-controlled ventilation, PEEP positive end-expiratory pressure, VT tidal volume, Pplat plateau pressure, RR respiratory rate, ∆P driving pressure, BIPAP/APRV biphasic positive airway pressure/airway pressure release ventilation, Phigh high pressure, Plow low pressure, UFH Unfractionated heparin, aPTT activated partial thromboplastin time, PK/PD pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamics, RASS richmond agitation-sedation scale, P0.1 drop in airway pressure observed during the first 100 ms of an inspiratory effort made against the occluded airway opening, Pven venous pressure (i.e. inlet pressure) on ECMO, Part arterial pressure (i.e., outlet pressure) on ECMO, ∆P on ECMO trans-membrane oxygenator pressure gradient or pressure drop, i.e., the difference betweenthe pressure of the blood at the inlet and at the outlet of the membrane lung, usually 10–50 mmHg. a Modified EOLIA settings with a set RR lower than in EOLIA