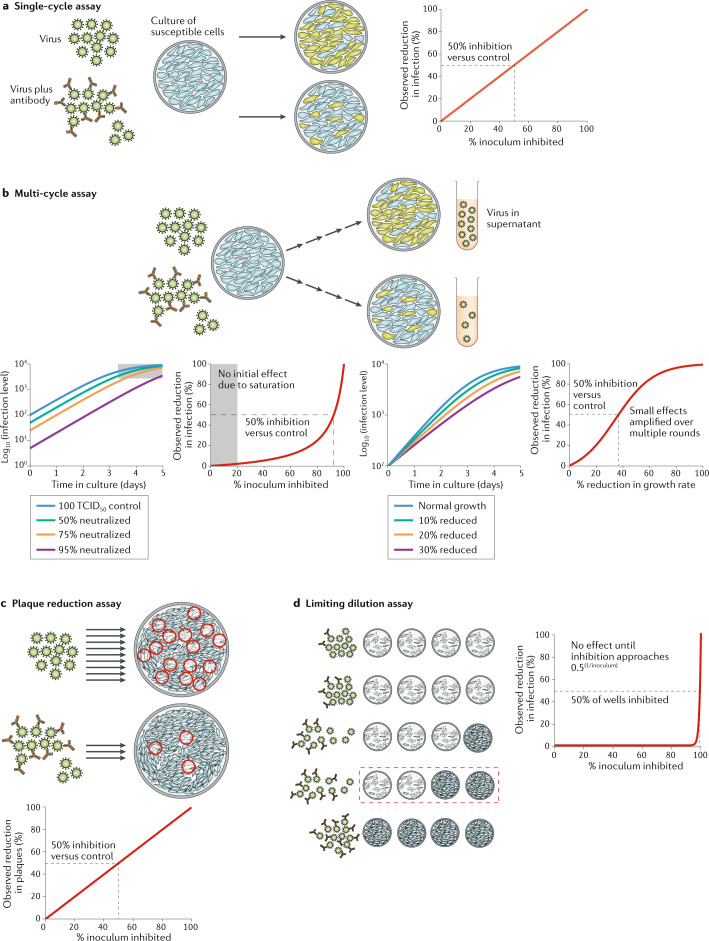
Fig. 1. In vitro assays for measuring viral inhibition.
a | Single-cycle pseudotyped virus assays involve co-incubation of virus and cells and measurement of the number of infected cells by a fluorescent reporter construct. They can provide a direct measure of the proportion of virus entry neutralized by serum or antibodies. b | Multi-cycle assays use either replication-competent pseudoviruses or native severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and measure the spread of infection over multiple cycles of infection in vitro. The level of infection can be measured using detection of a fluorescent reporter construct, viral antigen in infected cells or free virus in the supernatant. Some assays reach saturation before the end of the incubation and are thus insensitive to small changes in initial inoculum or viral growth rate. Once saturation is overcome, the fraction reduction in initial infectious viral levels is reflected as an equivalent fold-change in final viral levels (left hand panels). By contrast, small changes in viral growth rate are amplified over multiple rounds of infection, leading to large changes in final viral levels (right hand panels). c | Plaque reduction neutralization assays involve co-incubation of virus and antibody followed by plating out of virus onto an immobilized cell monolayer and incubation. The number of infectious virions remaining in the inoculum is enumerated by counting plaques of infected cells. d | An alternative limiting dilution approach involves co-incubation of antibody and virus followed by splitting into multiple wells to observe the proportion of wells infected. Cytopathic effect is commonly used as a read-out. The apparent IC50 (the concentration of antibody required to reduce infection to 50% of that seen in untreated control cultures) of the assay is highly dependent on the initial inoculum size. Inhibition of the cytopathic effect is only observed when the initial viral titres are reduced to <1 TCID50 (50% tissue culture infectious dose) in some wells. For this reason, limiting dilution-based assays can estimate a very different IC50 compared with single-cycle pseudotyped viral assays. Note that in the cytopathic effect assay, for a given input level of V0 infectious units, the IC50 occurs when the fraction of virions neutralized is 0.5(1/V0).