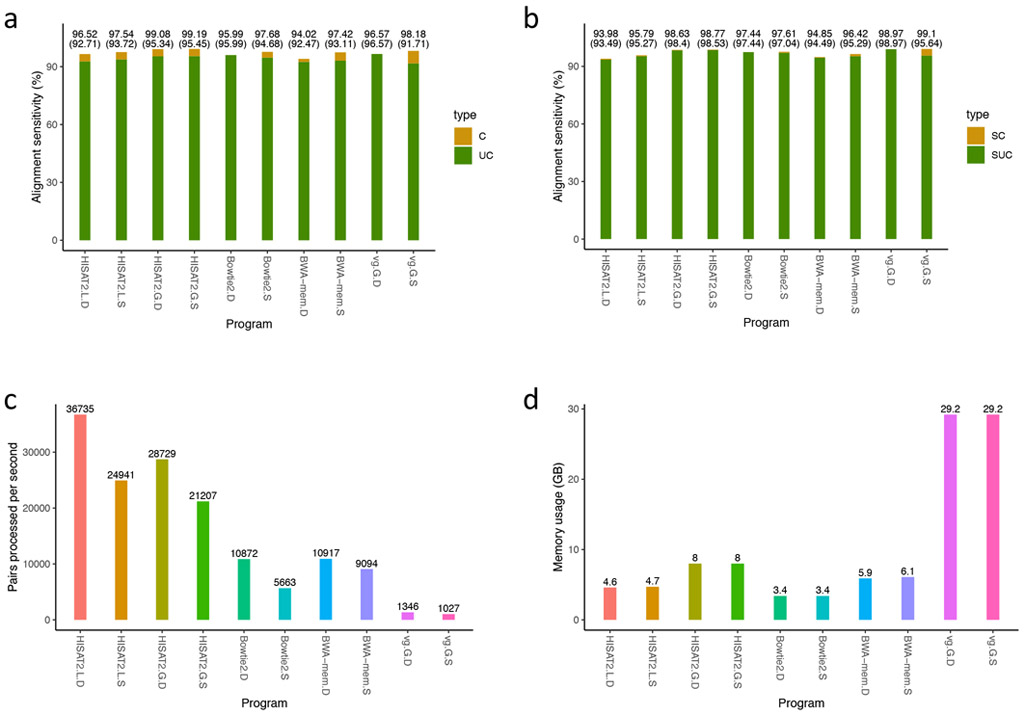
Figure 5.
Comparisons of HISAT2, Bowtie2, BWA-mem, and VG using 10 million simulated read pairs that include SNPs
Alignment sensitivity is defined as the number of correctly aligned read pairs divided by the total number of read pairs.
C: alignment sensitivity calculated based on any one of multiple alignments being correct.
UC: alignment sensitivity calculated based on pairs being uniquely aligned.
SC: alignment sensitivity similar to C, but calculated only for pairs with at least one read that includes one or more SNPs.
SUC: alignment sensitivity similar to UC, but calculated only for pairs with at least one read that includes one or more SNPs.
PPS: number of pairs processed per second.
The suffixes followed by program names stand for as follows: D for default alignment settings, S for sensitive alignment settings, L for linear genome alignment, and G for graph genome alignment.
We ran the programs on the same computer as described in Supplementary Table 7.