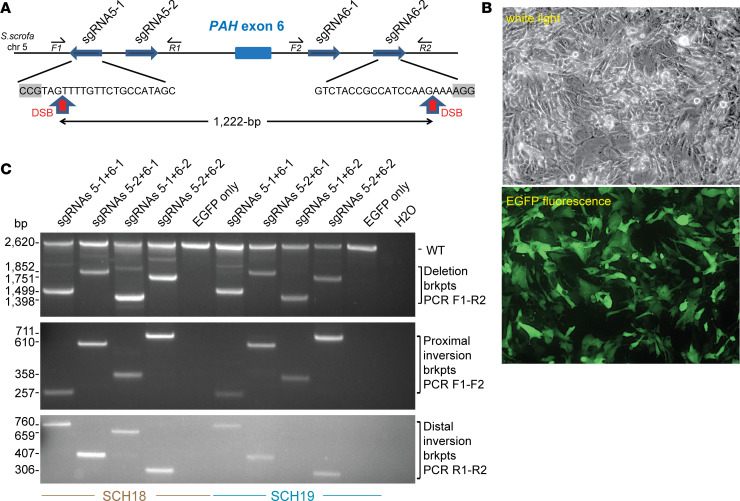
Figure 1. Strategy and optimization in vitro for CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing of the pig PAH gene.
(A) Strategy showing paired CRISPR sgRNA targeting to generate deletion or inversion of PAH exon 6. Key: thick directional blue arrows, sgRNAs targeting the sense or complementary strand of intron 5 or intron 6; small directional arrows, forward (F) or reverse (R) deletion and inversion genotyping PCR primers; red vertical arrows, DSB sites in optimal sgRNA5-1 and sgRNA6-2 at a position 3 nt 5′ of the PAM motif (gray boxes). (B) Representative images (white light and EGFP epifluorescence, original magnification, ×10) for transfection of the SCH18 line with plasmids encoding Cas9, CRISPR sgRNA5-1 + sgRNA6-2, and EGFP. (C) Deletion and inversion PCR assays to detect exon 6 genome editing in SCH lines. Top: Deletion PCR assay with genotyping primers F1 and R2, for SCH18 and SCH19 cells transfected with pairs of sgRNA vectors plus EGFP or EGFP only as a control. Deletion breakpoints (brkpts) are only amplified in cells transfected with Cas9/sgRNA vectors whereas the WT band is detected in all samples. Middle and bottom: Inversion PCR assays for proximal and distal inversion breakpoints using primer pairs F1 and F2 or R1 and R2, respectively. Inversion breakpoints are detected in cells transfected with pairs of Cas9/sgRNA vectors indicating robust genome editing and NHEJ repair using the inverted exon 6 segment to bridge the DSB sites.