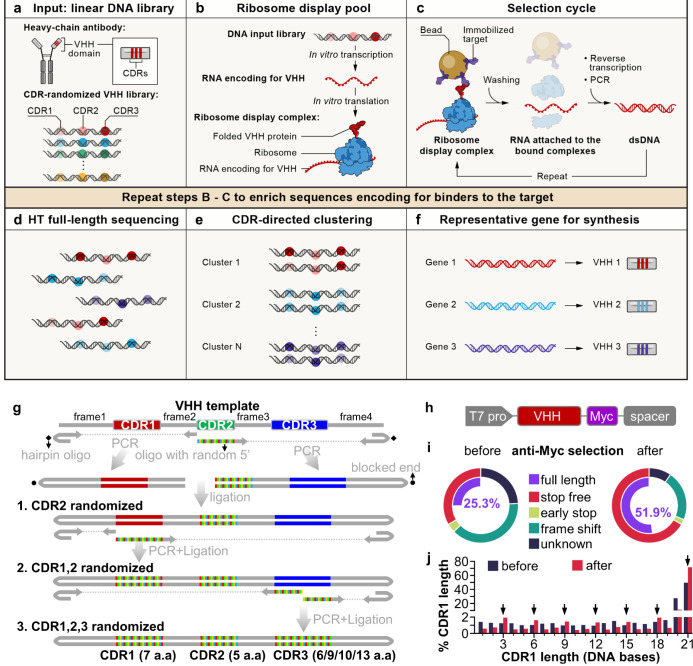
Fig. 1. A cell-free antibody engineering platform for rapid isolation of antibodies from large synthetic libraries.
(a) The workflow takes linear DNA library as input. (b) Ribosome display links genotype (RNAs transcribed from DNA input library that are stop codon free, and stall ribosome at the end of the transcript) and phenotype (folded VHH protein tethered to ribosomes due to the lack of stop codon in the RNA). (c) Selection cycle that enriches DNA encoding for VHHs that binds immobilized targets. (d) High throughput sequencing of full-length VHHs. (e) Sequences are grouped into clusters based on similarity of their CDRs, each cluster is distinct and represent a unique binding family. (f) The system outputs one representative sequence from each cluster to be synthesized and characterized for specific downstream applications. (g) Workflow for generating VHH library. VHH CDR randomization was introduced by PCR using a hairpin oligo (blocks DNA end from ligation) and an oligo with random 5’ sequence, followed by orientation-controlled ligation. Three successive PCR plus ligation cycles randomizes all three CDRs. (h) The final DNA library sequence structure. (i) One round of ribosome display and anti-Myc selection was performed after randomization of CDR1 and CDR2. The pie chart shows percentage of indicated sequence categories before and after anti-Myc selection. (j) Length distribution of DNA region encoding CDR1 of the VHH library before and after anti-Myc selection. Arrows indicate all correct-frame lengths showing increased percentage after anti-Myc selection.