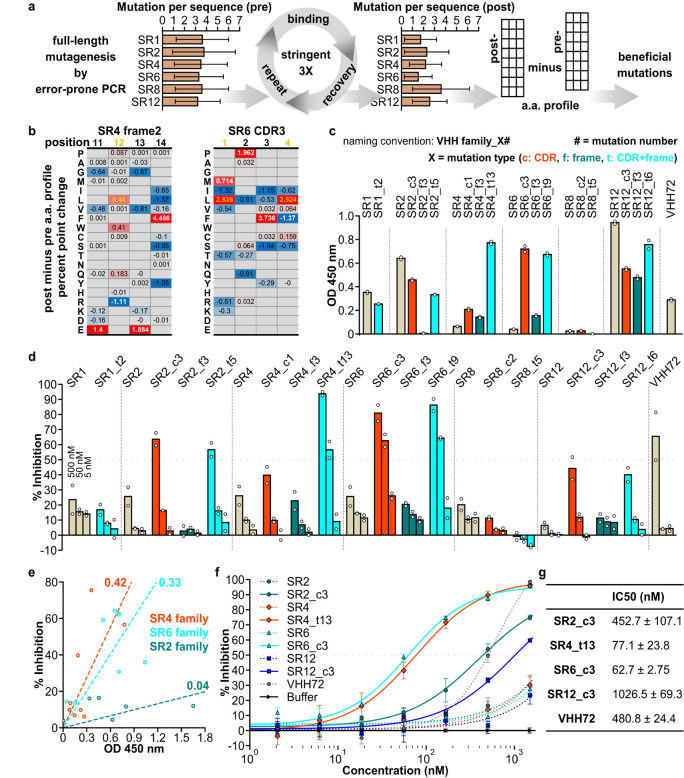
Fig. 3. An affinity maturation strategy enhances binding and neutralization properties of synthetic VHHs.
(a) Affinity maturation workflow. (b) Two representative sections of position-wise post-minus pre-affinity maturation amino acid percent point change profile. White values indicate the original amino acid, yellow values indicate the beneficial mutation. Empty positions indicate amino acids not detected in either the pre- or post-selection libraries. (c) ELISA assay of VHH variants. (d) SARS-CoV-2 S pseudotyped lentivirus neutralization assay of VHHs on HEK293T expressing ACE2 and TMPRSS2. For (c) and (d), data shown are two technical replicates, bars indicate the average of data, circles indicate values of each replicate. (e) Scatter plot of ELISA assay absorbance versus pseudotyped lentivirus neutralization as percent infection inhibited. VHH concentration for both assays were 50 nM. Values are average of two technical replicates. Numbers on linear fitting lines were r2 value for data within each family. (f) Dose-response curve for neutralization of pseudotyped lentiviral infection by VHHs. Markers are average of three technical replicates, error bars are standard deviation. (g) IC50 calculated from data in (f), presented as mean ± standard deviation.