Table 2.
Rhodium-Catalyzed Enantioselective Si–H Bond Insertion of Diphenyl Diazomethanes D13–D30
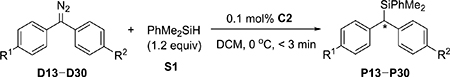 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entrya | R1 | R2 | Δσp (R1-R2)b | product | yield(%) | ee(%) |
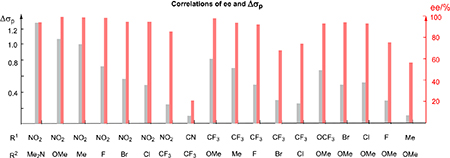
| 1 | NO2 | NMe2 | 1.38 | P13 | 66 | 96 |
| 2 | NO2 | OMe | 1.05 | P14 | 78 | 99 |
| 3 | NO2 | Me | 0.95 | P15 | 87 | 99 |
| 4 | NO2 | F | 0.72 | P16 | 86 | 98 |
| 5 | NO2 | Br | 0.55 | P17 | 80 | 95 |
| 6 | NO2 | CI | 0.5 | P18 | 88 | 96 |
| 7 | NO2 | CF3 | 0.24 | P19 | 58 | 86 |
| 8 | CN | CF3 | 0.12 | P20 | 42 | 36 |
| 9 | CF3 | OMe | 0.81 | P21 | 78 | 98 |
| 10c | CF3 | Me | 0.71 | P22 | 85 | 94(S) |
| 11c | CF3 | F | 0.48 | P23 | 63 | 92 |
| 12c | CF3 | Br | 0.31 | P24 | 71 | 67 |
| 13c | CF3 | CI | 0.26 | P25 | 73 | 76(R) |
| 14 | OCF3 | OMe | 0.62 | P26 | 58 | 93 |
| 15 | Br | OMe | 0.50 | P27 | 58 | 94 |
| 16 | CI | OMe | 0.55 | P28 | 59 | 93 |
| 17c | F | OMe | 0.33 | P29 | 43 | 77(R) |
| 18 | Me | OMe | 0.10 | P30 | 40 | 56 |
 | ||||||
Reaction conditions: hydrazone (0.2 mmol), MnO2 (3.5 equiv), MgSO4, DCM, rt, 5–6 h; then PhMe2SiH (1.2 equiv), C2 (0.1 mol %), DCM, 0 °C. Isolated yields were given. The ee values were determined by chiral HPLC analysis.
The Hammett substituent constant difference for para substituents.
The ee value was determined by the corresponding alcohol obtained through the oxidation of Si–H insertion product. A plot of log(er) vs Δσp (R1-R2) is shown in Figure S2.
