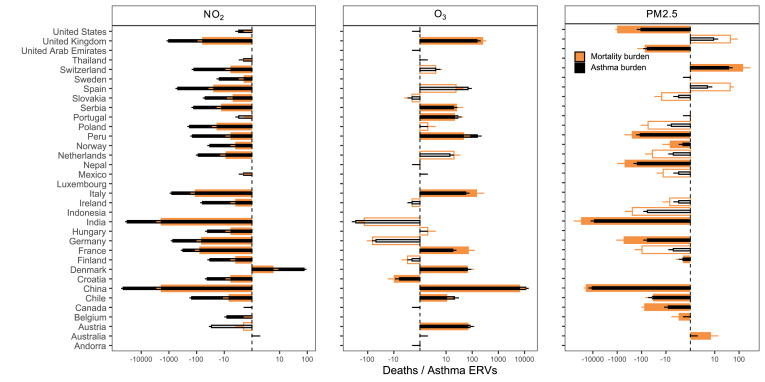
Fig. 1.
Post-lockdown health burden changes attributable to air pollution. Air pollution anomalies during lockdown are converted to changes in mortality and asthma exacerbation (n = 34 countries). Total health burden avoided (-ve) and incurred (+ve) values are presented with bars along a log-transformed x-axis. 95% uncertainty intervals are marked with error bars. Hollow bars represent estimates where the change in pollutant concentrations were not significant (p > 0.05) after accounting for weather variations.