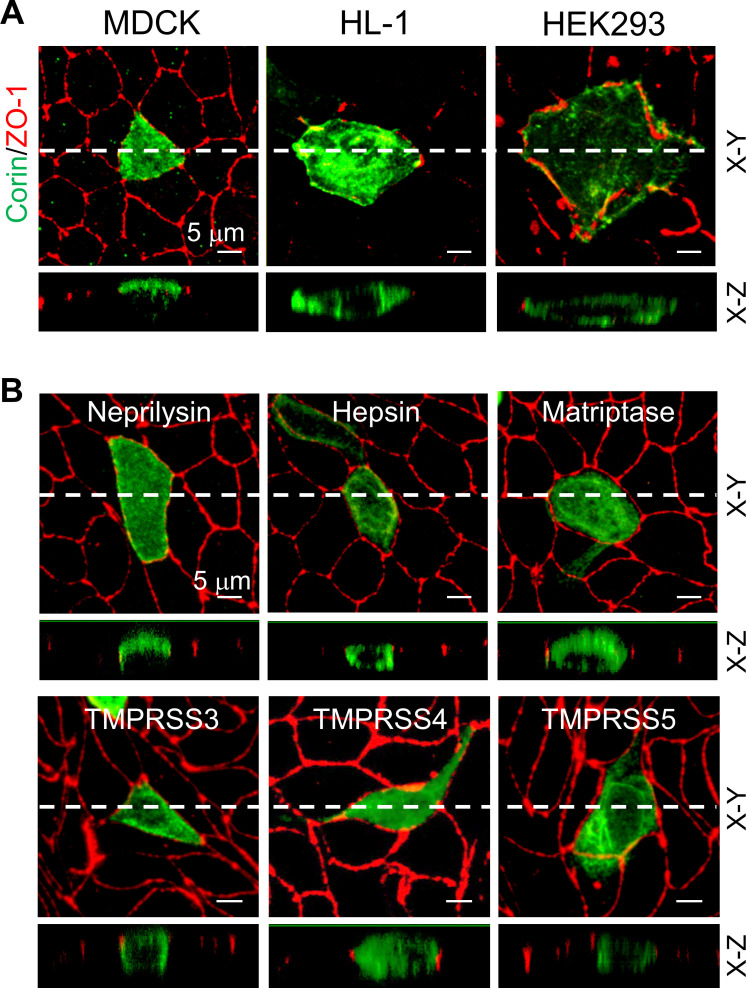
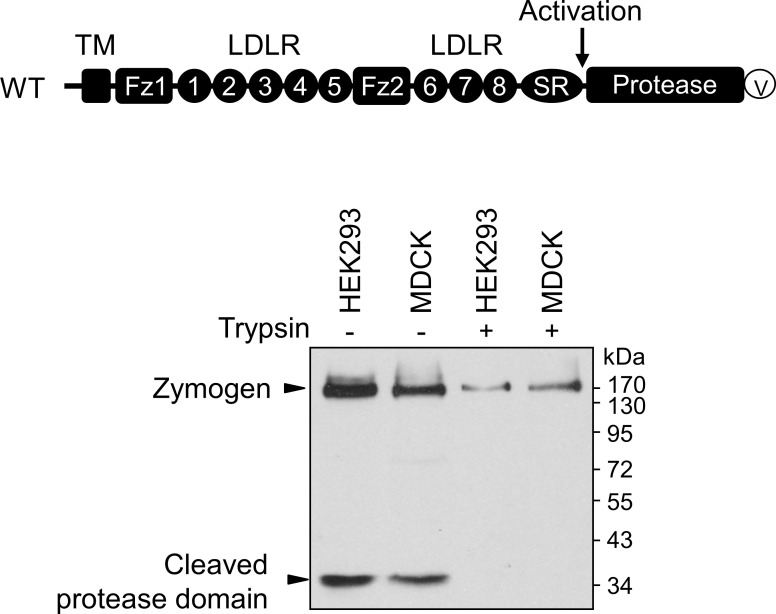
Figure 1. Expression of corin and other selected proteases in MDCK, HL-1, and HEK293 cells.
(A) MDCK (left), HL-1 (middle), and HEK293 (right) cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing corin. After 72 hr, immunostaining was done to examine corin (green) and ZO-1 (red) (an indicator of the apicolateral tight junction) expression with confocal microscopy. X-Y and X-Z views are shown in top and lower panels, respectively. (B) Neprilysin, hepsin, matriptase, and TMPRSS3-5 (green) were expressed in transfected MDCK cells. Immunostaining and confocal microscopy were used to examine protein expression on apical and basolateral membranes. X-Y and X-Z views are shown in top and lower panels, respectively. Each image represents the data from five experiments. Scale bars: 5 μm.