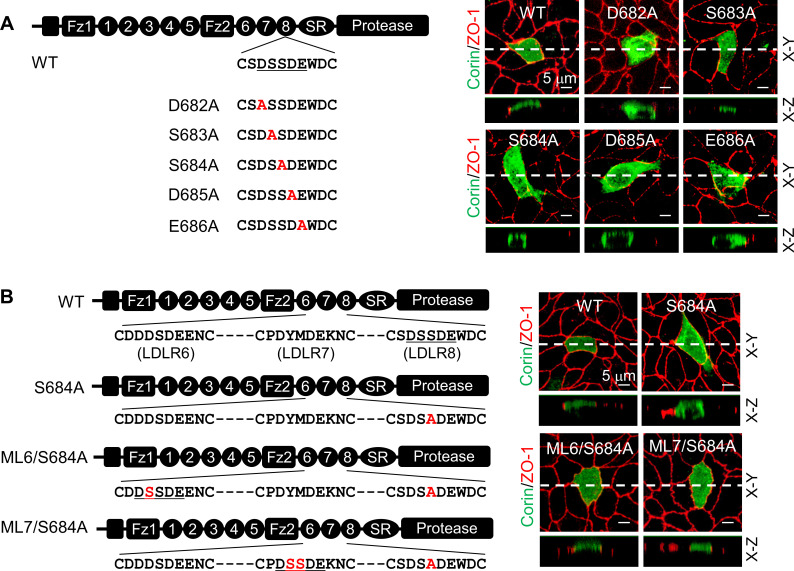
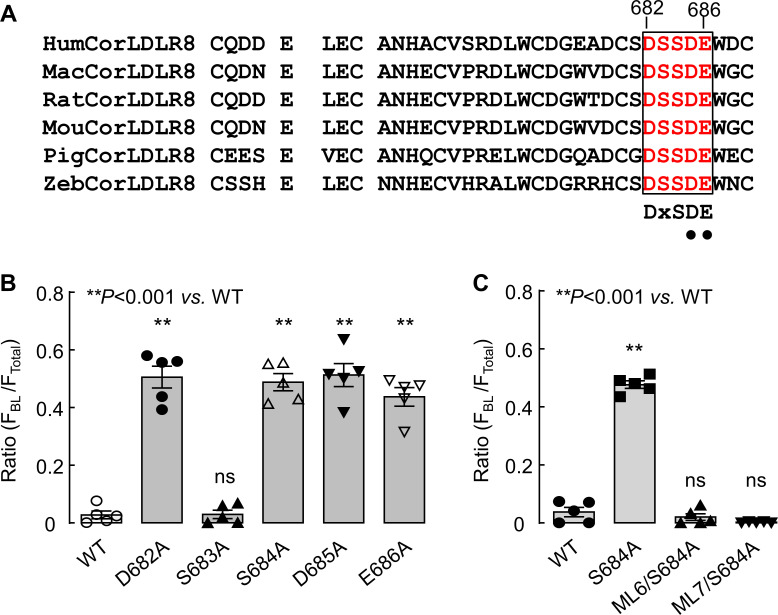
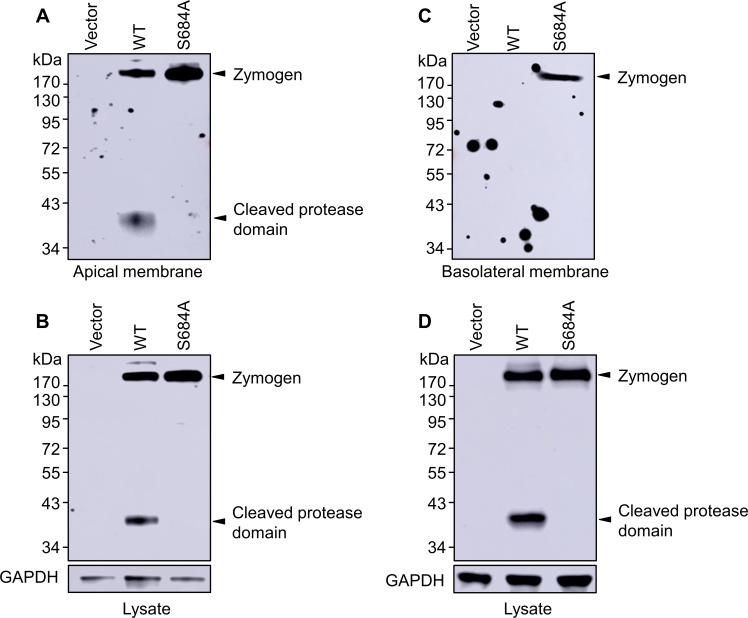
Figure 4. Expression of corin mutants with point mutations in the DSSDE motif in LDLR8 module.
(A) Corin wild-type (WT) and mutants with point mutations at indicated positions (D682A, S683A, S684A, D685A, and E686A), indicated in red, were expressed in MDCK cells. Corin expression (green) on apical and basolateral membranes was examined by immunostaining and confocal microscopy with X-Y (top panels) and X-Z (lower panels) views. (B) Corin WT and S684A mutants without (S684A) or with the DSSDE motif created in LDLR6 (ML6/S684A) or LDLR7 (ML7/S684A) module expressed in MDCK cells were examined by immunostaining and confocal microscopy. X-Y (top panels) and X-Z (lower panels) views are indicated. Each image represents the data from five experiments. Scale bars: 5 μm.