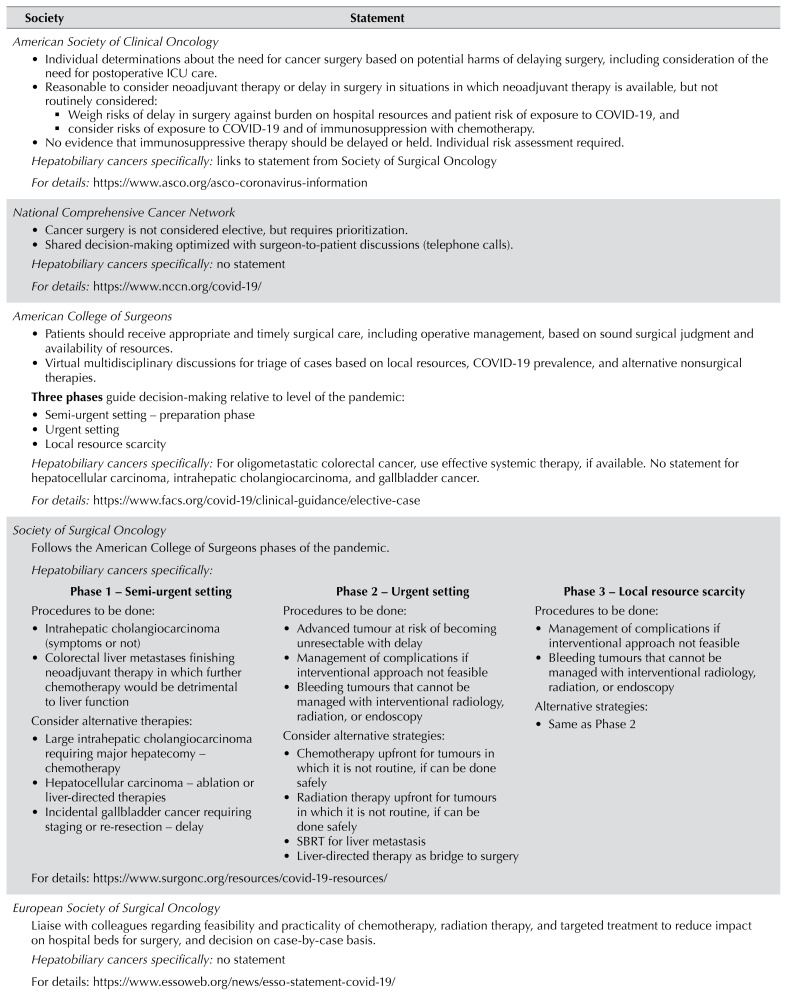
American Society of Clinical Oncology
Individual determinations about the need for cancer surgery based on potential harms of delaying surgery, including consideration of the need for postoperative ICU care. -
Reasonable to consider neoadjuvant therapy or delay in surgery in situations in which neoadjuvant therapy is available, but not routinely considered:
▪ Weigh risks of delay in surgery against burden on hospital resources and patient risk of exposure to COVID-19, and ▪ consider risks of exposure to COVID-19 and of immunosuppression with chemotherapy.
No evidence that immunosuppressive therapy should be delayed or held. Individual risk assessment required. Hepatobiliary cancers specifically: links to statement from Society of Surgical Oncology
For details:
https://www.asco.org/asco-coronavirus-information
|
|
National Comprehensive Cancer Network
Cancer surgery is not considered elective, but requires prioritization. Shared decision-making optimized with surgeon-to-patient discussions (telephone calls).
|
Hepatobiliary cancers specifically: no statement
For details:
https://www.nccn.org/covid-19/
|
|
American College of Surgeons
Patients should receive appropriate and timely surgical care, including operative management, based on sound surgical judgment and availability of resources. Virtual multidisciplinary discussions for triage of cases based on local resources, COVID-19 prevalence, and alternative nonsurgical therapies. Three phases guide decision-making relative to level of the pandemic:
Hepatobiliary cancers specifically: For oligometastatic colorectal cancer, use effective systemic therapy, if available. No statement for hepatocellular carcinoma, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, and gallbladder cancer.
For details:
https://www.facs.org/covid-19/clinical-guidance/elective-case
|
|
Society of Surgical Oncology
Follows the American College of Surgeons phases of the pandemic.
Hepatobiliary cancers specifically:
|
| Phase 1 – Semi-urgent setting |
Phase 2 – Urgent setting |
Phase 3 – Local resource scarcity |
Procedures to be done:
Consider alternative therapies:
Large intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma requiring major hepatecomy – chemotherapy Hepatocellular carcinoma – ablation or liver-directed therapies Incidental gallbladder cancer requiring staging or re-resection – delay
|
Procedures to be done:
Advanced tumour at risk of becoming unresectable with delay Management of complications if interventional approach not feasible Bleeding tumours that cannot be managed with interventional radiology, radiation, or endoscopy Consider alternative strategies:
Chemotherapy upfront for tumours in which it is not routine, if can be done safely Radiation therapy upfront for tumours in which it is not routine, if can be done safely SBRT for liver metastasis Liver-directed therapy as bridge to surgery
|
Procedures to be done:
Management of complications if interventional approach not feasible Bleeding tumours that cannot be managed with interventional radiology, radiation, or endoscopy Alternative strategies:
|
| For details: https://www.surgonc.org/resources/covid-19-resources/
|
|
European Society of Surgical Oncology
Liaise with colleagues regarding feasibility and practicality of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted treatment to reduce impact on hospital beds for surgery, and decision on case-by-case basis.
Hepatobiliary cancers specifically: no statement
For details: https://www.essoweb.org/news/esso-statement-covid-19/
|
Americas Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association
Follows the American College of Surgeons phases of the pandemic.
Hepatobiliary cancers specifically:
Consider patient comorbidities and age to assess relative risks and benefits with potential exposure to COVID-19 compared with alternative treatment options. Consider changes in resources available at various stages of the pandemic. For patients facing a potentially prolonged hospital stay or at higher risk for complications requiring ICU management, surgery should be timed to available resources.
|
| Phase 1 – Semi-urgent setting |
Phase 2 – Urgent setting | Phase 3 – Local resources scarcity |
Hepatocellular carcinoma – hepatectomy, transplant, ablation Colorectal liver metastases – hepatectomy for intermediate-acuity surgery and healthy patient, chemotherapy for intermediate-acuity surgery and unhealthy patient Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma – hepatectomy for intermediate-acuity surgery and healthy patient, chemotherapy for intermediate-acuity surgery and unhealthy patient Hilar cholangiocarcinoma – resection or transplantation as indicated
|
Hepatocellular carcinoma – delay definitive therapy; TACE ablation or observation Colorectal liver metastases – chemotherapy Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma – chemotherapy or embolic therapy Hilar cholangiocarcinoma – chemotherapy, chemoradiation, or transfer to a facility with more resources
|
| For details:
https://www.sages.org/sages-ahpba-recommendations-surgical-management-of-hpb-cancer-covid-19/
|