Figure 3. The reduced activity of LCAD K333Q is caused by impaired FAD binding.
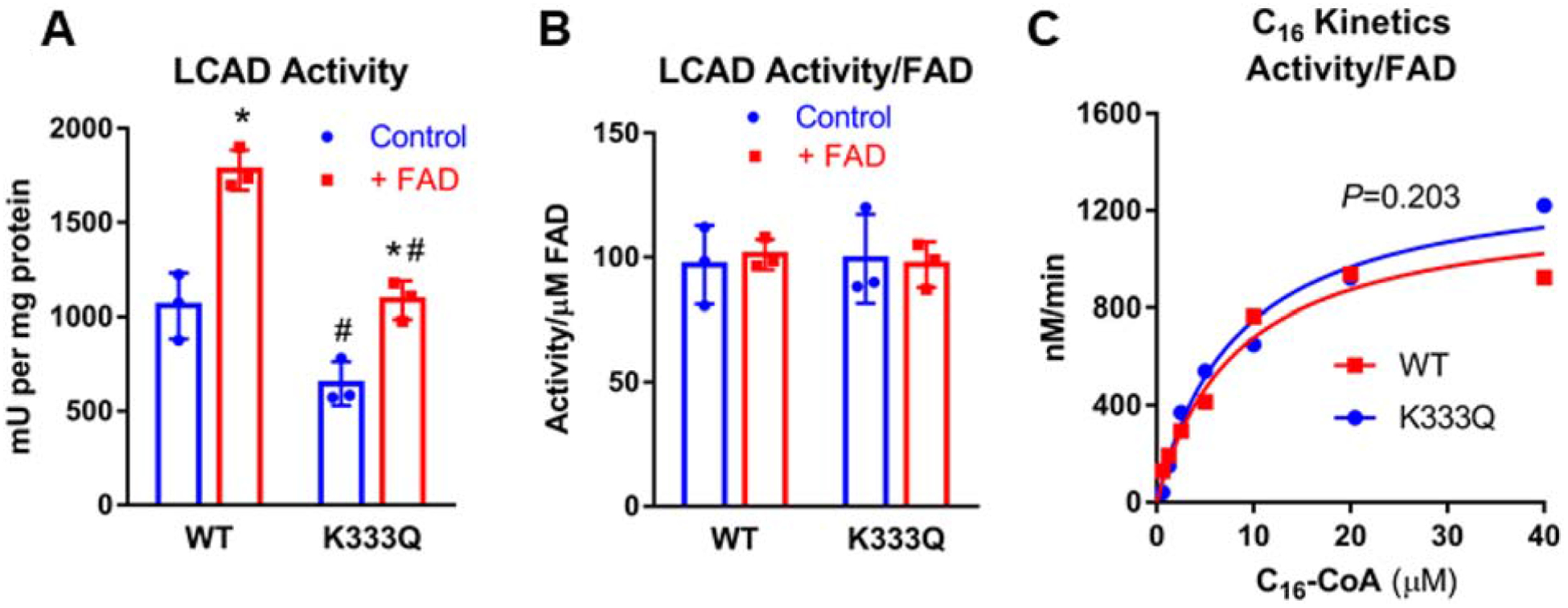
A) Incubation of recombinant LCAD proteins with free FAD increases the ACAD activity of both the WT and K333Q enzymes, but K333Q is only partially rescued. B) Normalizing the activity values from panel A by FAD content rather than protein eliminates the differences in activity, indicating that the loss of activity in K333Q as well as the gain of activity upon FAD incubation are solely a consequence of the amount of FAD bound to the enzymes. C) wild-type LCAD and K333Q are kinetically indistinguishable when activity values are normalized to FAD content rather than protein concentration. Assays were conducted in triplicate for panels A, B and duplicate for panel C.
