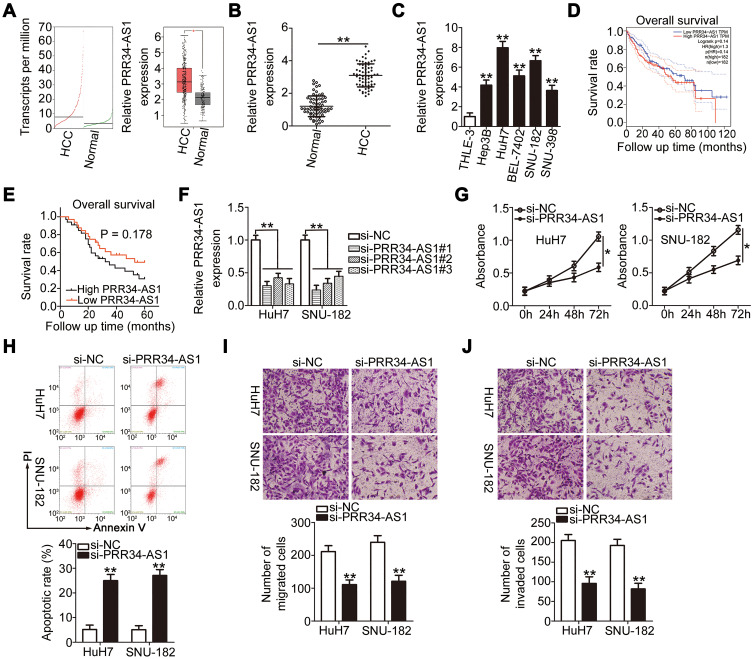
Figure 1.
Knockdown of PRR34-AS1 inhibits HCC progression. (A) PRR34-AS1 expression in HCC and normal liver tissues from the TCGA and GTEx databases. (B) RT-qPCR detection of the expression of PRR34-AS1 in 65 pairs of HCC and adjacent normal tissues. (C) RT-qPCR analysis was used to determine PRR34-AS1 expression in HCC cell lines (Hep3B, HuH7, BEL-7402, SNU-182, and SNU-398) and transformed Human Liver Epithelial-3 (THLE-3). (D) TCGA and GTEx databases were used to analyze the overall survival rates of patients with HCC with high or low PRR34-AS1 expression. (E) Kaplan–Meier analysis was conducted to determine the correlation between PRR34-AS1 expression and the overall survival rate of patients with HCC. (F) HuH7 and SNU-182 cells were transfected with si-PRR34-AS1 or si-NC. The knockdown efficiency of si-PRR34-AS1 was assessed via RT-qPCR. (G and H) CCK-8 assays and flow cytometric analysis were used to detect the proliferation and apoptosis of HuH7 and SNU-182 cells after PRR34-AS1 depletion, respectively. (I and J) Transwell cell migration and invasion assays were used to determine the effects of PRR34-AS1 silencing on the migratory and invasive capabilities of HuH7 and SNU-182 cells (x200 magnification). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.