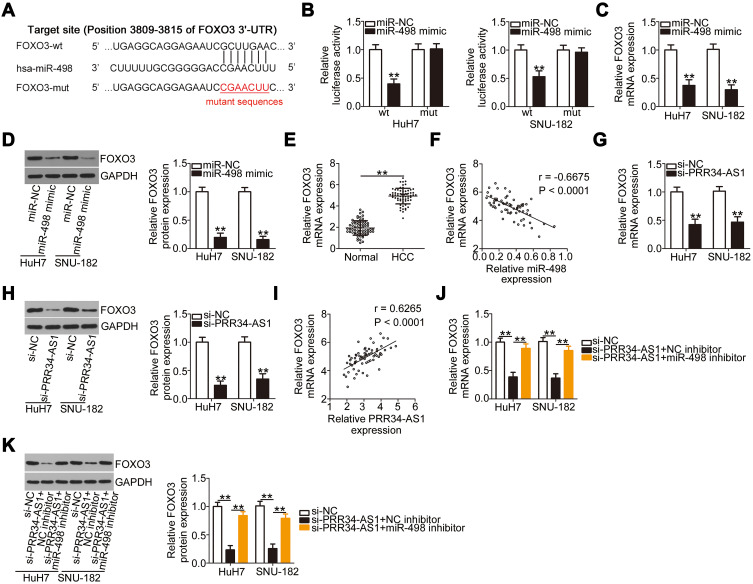
Figure 4.
FOXO3 is directly targeted by miR-498 in HCC cells and under the regulation of PRR34-AS1. (A) The complementary binding site between miR-498 and FOXO3 was predicted via bioinformatic analysis. (B) Luciferase reporter assays were performed in HuH7 and SNU-182 cells cotransfected with miR-498 mimic or miR-NC and wt-FOXO3 or mut-FOXO3. (C and D) The mRNA and protein expression levels of FOXO3 were detected in HuH7 and SNU-182 cells after miR-498 upregulation. (E) The mRNA level of FOXO3 in the 65 pairs of HCC and adjacent normal tissues was tested via RT-qPCR. (F) Pearson’s correlation coefficient analysis illustrated the correlation between miR-498 and FOXO3 mRNA expression in the 65 HCC tissues. (G and H) The regulatory effects of PRR34-AS1 deficiency on FOXO3 mRNA and protein levels in HuH7 and SNU-182 cells were determined via RT-qPCR and Western blotting. (I) The relationship between PRR34-AS1 and FOXO3 mRNA expression in the 65 HCC tissues was tested using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. (J and K) HuH7 and SNU-182 cells were transfected with miR-498 inhibitor or NC inhibitor in the presence of si-PRR34-AS1, and changes in the expression of FOXO3 mRNA and protein were examined via RT-qPCR and Western blotting, respectively. **P < 0.01.