Table 1.
High potency mitotic kinase inhibitors stalled in late-stage clinical trials due to significant adverse events.
| Drug | Structure | Target (Ki) | Farthest clinical stage | Dose limiting toxicity | Best clinical response rate | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alisertib | 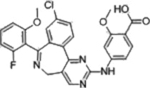 |
AURKA (1.2 nM) | Phase III (2012–2015) NCT01482962 |
Febrile neutropenia | 17% in aggressive B-cell Lymphoma | [23] |
| Ispinesib |  |
Eg5/KIF11 (1.7 nM) | Phase II (2004–2006) NCT00089973 |
Febrile neutropenia, vomiting | 0% in Malignant melanoma | [24–26] |
| Dinaciclib | 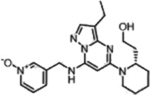 |
CDK2 (1 nM) CDK5 (1 nM) CDK1 (3 nM) CDK9 (4 nM) |
Phase I (2016–2018) NCT02684617 NCT03484520 |
Neutropenia, Pneumocytis | 11% PR in multiple myeloma | [27,28] |
| GSK461364 | 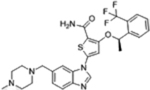 |
PLK1 (2.2 nM) | Phase I (2007–2009) NCT00536835 |
Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombic eboli, myelosuppression | 0% in solid tumors | [29–30] |
| BAY1217389 | 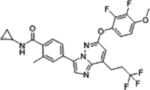 |
TTK (0.63 nM) | Phase I (2015–2019) NCT02366949 |
Hematologic toxicity, neutropenia, | N/A | [31] |
An overview of structures, corresponding target affinities, and farthest progression in clinical trials for several potent mitotic kinase inhibitors is shown. Even with single-digit nanomolar Kis, major dose-limiting toxicities are still observed, stalling these trials. According to RECIST criteria, none of these included drugs achieved a complete response (CR) at toxicity-limiting doses. The best clinical response rates (objective, PR) are less than 20%.
