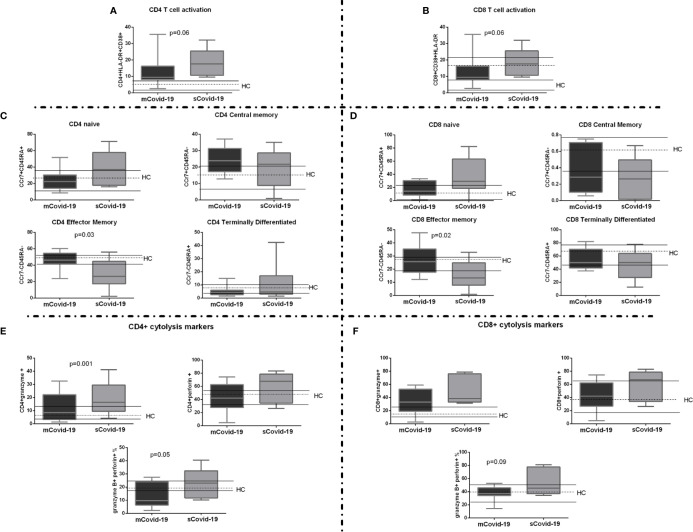
Figure 3.
T-cell activation, maturation, and cytolysis markers among COVID-19 patients. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated and analyzed from blood samples of 40 COVID-19 patients [severe Covid-19 (sCovid-19) n = 20 and mild Covid-19 (mCovid-19) n = 20]. (A, B) HLA-DR+CD38+ expressing both in CD4+ and CD8 T-cells were significantly increase in (sCovid-19) compared to (mCovid-19) (p = 0.06 and p = 0.06). (C, D) We observed no difference in naïve (CCR7+CD45RA+), CM: central memory (CCR7+CD45RA−) and TD: terminally differentiated (CCR7−CD45RA+). sCOVID-19 patients showed significantly lower CD4+ and CD8+ EM: effector memory (CCR7−CD45RA−) (p = 0.03 and p = 0.02). (E) Compared to mCovid-19, sCovid-19 patients tended to have a higher number of CD4+granzyme+ cells (p = 0.001). We fail to observe any modification in CD4+ perforin + cells. The number of CD4+granzyme+perforin+ cells was higher in sCovid-19 patients when compared to mCovid-19 (p = 0.05). (F) No major differences in CD8+ granzyme+ and CD8+ perforin+ were observed between mCovid-19 and sCovid-19. A non-significant tendency towards increased CD8+ granzyme-perforin+ frequency was observed in sCovid-19 patients in comparison to mCovid-19 (p = .09). In each graph the columns represent the median values, while the error bars indicate the 10th–90th percentile range. Dotted lines indicate the median levels and solid lines indicate 10th–90th percentile range of healthy controls (HCs) from archived material. Comparison between groups (sCovid-19 vs mCovid-19) Mann–Whitney test.