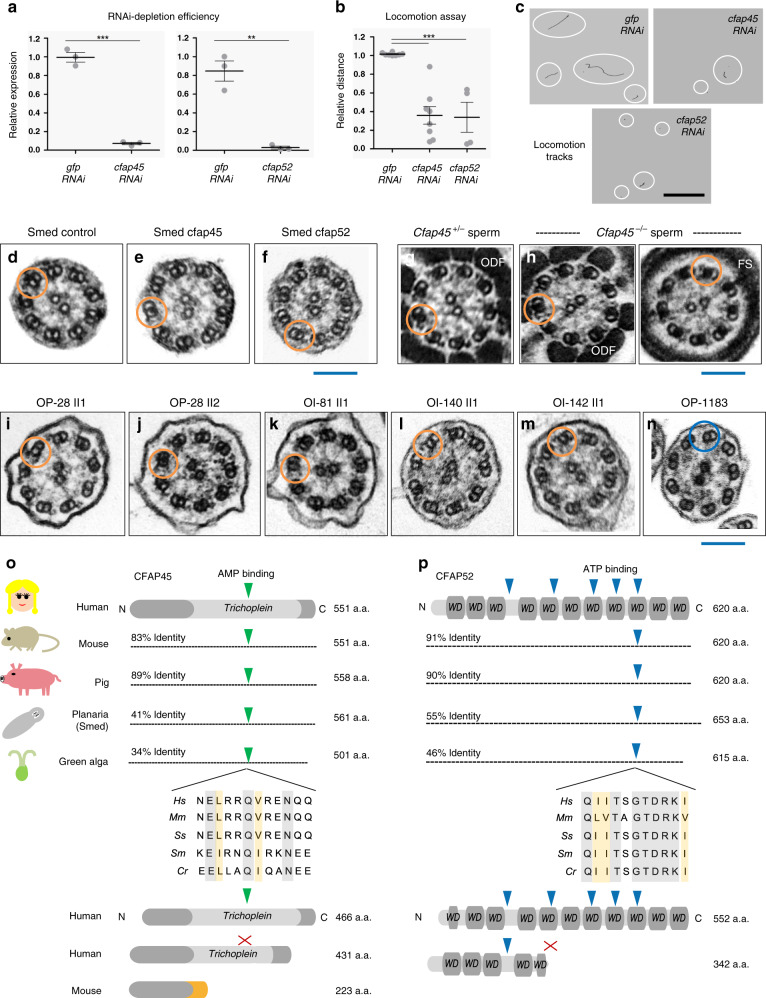
Fig. 5. CFAP45 and CFAP52 orthologs have a conserved ciliary function.
a RNAi efficiently depletes cfap45 and cfap52 in Schmidtea mediterranea (Smed) (n = 3 animals over three independent experiments for cfap45, cfap52, and gfp control); data are the means ± SEM; significance is assessed by two-tailed t-test (***p < 0.0001; **p = 0.0017). b In contrast to gfp- (n = 62 animals over eight independent experiments), the locomotion of cfap45- (n = 65 animals over eight independent experiments) and cfap52-RNAi planarians (n = 33 animals over four independent experiments) is significantly impaired in 0.6% low-melting agarose; data are the means ± SEM; significance is assessed by two-tailed t-test (***p < 0.0001). c Representative locomotion tracks (white circles) of gfp, cfap45, and cfap52-RNAi planarians; black scale bar equals 33 mm. d–n CFAP45- and CFAP52-deficient axonemes across eukaryota show normal ciliary ultrastructure. Similar to gfp control (d), TEM shows normal ciliary ultrastructure in cfap45 (e) and cfap52 (f) RNAi planarians. n = 8 images from two experiments for gfp, cfap45, and cfap52. Similar to heterozygous littermates (g), Cfap45−/− flagellar axonemes show normal ultrastructure in the midpiece (ODF outer dense fiber) and principal piece (FS fibrous sheath) regions, respectively (h). n = 8 images from two experiments for Cfap45+/− and Cfap45−/− sperm. Axonemal ultrastructure of respiratory cilia from CFAP45-deficient individual OP-28 II1 (i) is indistinguishable from healthy sibling OP-28 II2 (j) as well as CFAP52-deficient individuals OI-81 (k), OI-140 (l) and OI-142 (m). For reference, PCD individual OP-1183 (LRRC6; p.Gln188*hom.) shows a typical ciliary ultrastructure lacking both ODAs and IDAs (n). n = 6 images from 1 experiment for (i–n). Orange rings indicate detectable ODA and IDA pairs; blue ring indicates absent ODA and IDA pairs. Blue scale bars equal 100 nm. Potential AMP (green arrowhead) and ATP-binding (blue arrowhead) sites are conserved in CFAP45 (o) and CFAP52 (p) orthologs, respectively, in an isoform-specific manner. See also Fig. 1g–j and Supplementary Fig. 5g, h. Protein alignments highlight identity (gray shade) and similarity (orange shade). Red “X” indicates no predicted binding site.