Fig. 1. Effect of PP1α overexpression on GR activity and nuclear translocation.
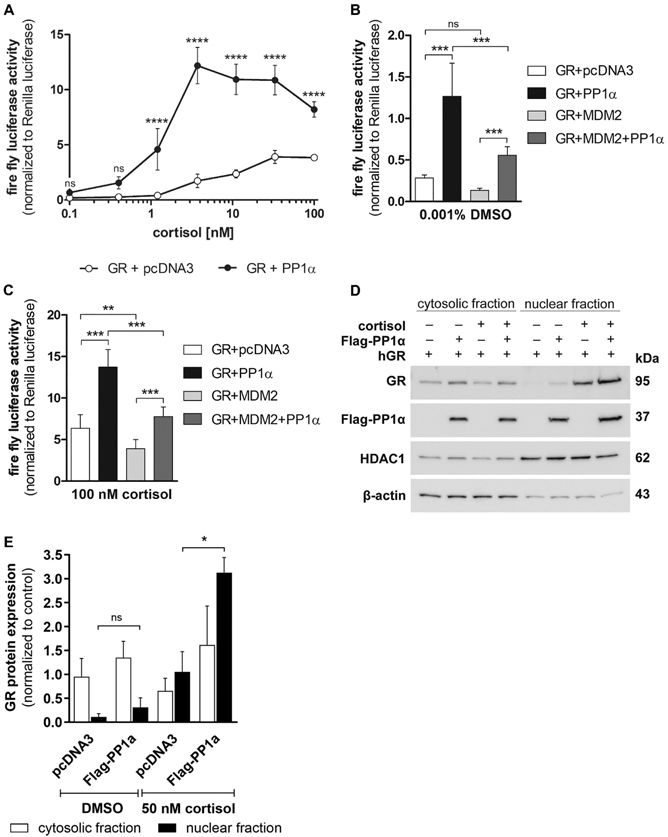
(A, B and C) HEK-293 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids coding for GR with or without PP1α, a luciferase reporter gene and a Renilla luciferase transfection control. Empty vector pcDNA3.1 was supplemented to equalize the total amount of DNA in the transfection. After 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated with vehicle or increasing concentrations of cortisol (A) for another 24 h. The luciferase reporter activity was normalized to the internal Renilla control. (B and C) Same as (A) but with co-transfection of MDM2. Data represent mean ± SD from at least two independent experiments, each performed in triplicate, ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, ns not significant. (D and E) HEK-293 cells were transfected with GR, with and without PP1α for 24 h, incubated overnight in charcoal-treated medium and then exposed to vehicle or 50 nM cortisol for 1 h. Cytosolic and nuclear fractions were analyzed by Western blot using antibodies against GR and the Flag-tag on PP1α. As controls, the fractions were reprobed with ant-β-actin (cytosolic) and anti-HDAC1 (nuclear) antibodies. A representative blot (D) and analysis of band density (E) from two independent experiments are shown. Values are depicted as mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, ns not significant.
