Fig. 2. Impact of PP1α knockdown on endogenous GR protein expression, translocation and GC-induced transcripts.
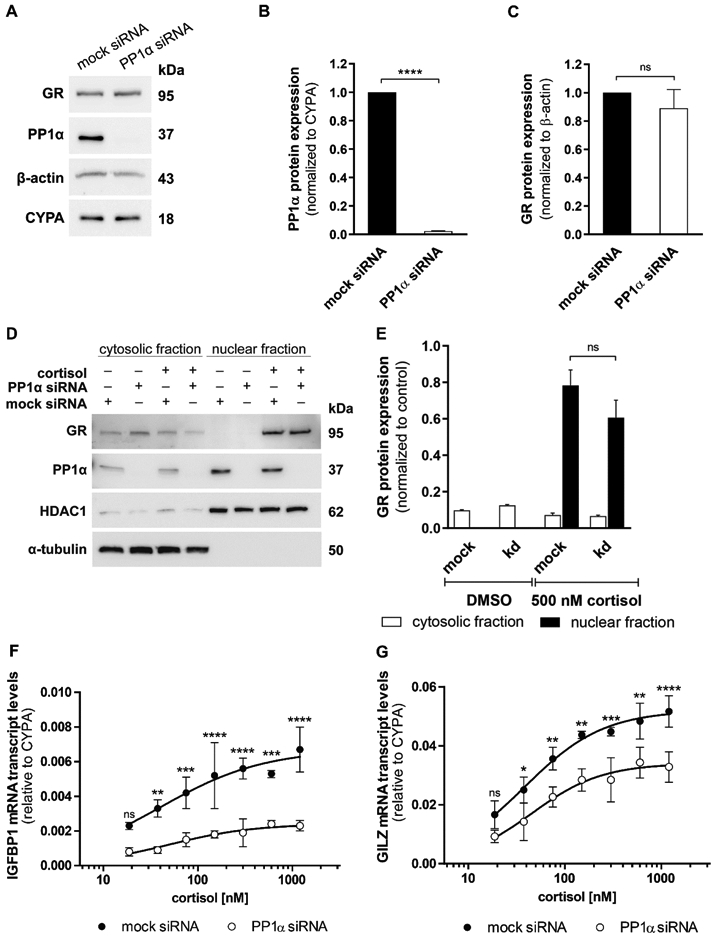
(A, B and C) Western blot analysis for protein expression of GR and PP1α was performed after mock or anti-PP1α siRNA treatment in A549 cells. A representative blot (A) and densitometry analysis of PP1α (B) and GR (C) from three independent experiments are shown. Data are normalized to mock siRNA samples (mean ± SD, ****P < 0.0001, ns not significant). (D and E) A549 cells were transfected with mock or anti-PP1α siRNA for 48 h, incubated overnight in serum-free medium and treated with vehicle or 500 nM cortisol for 1 h. Western blot analysis for cytosolic and nuclear fractions was performed using antibodies against GR and PP1α. As controls, the fractions were reprobed with anti-α-tubulin (cytosolic) and anti-HDAC1 (nuclear) antibodies. A representative blot (D) and analysis of band density (E) from two independent experiments are shown. Values are presented as mean ± SD, ns not significant. (F and G) At 48 h after knockdown of PP1α, A549 cells were cultured in steroid-free medium overnight prior to incubation with vehicle or increasing concentrations of cortisol (18.75 nM - 1200 nM) for 4 h. Cortisol-induced transcription of the GR-responsive genes IGFBP1 (F) and GILZ (G) was measured by RT-qPCR in technical triplicate for each sample. Data are represented as 2−ΔCt mean ± SD from three independent experiments, ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, ns not significant.
