Figure 7.
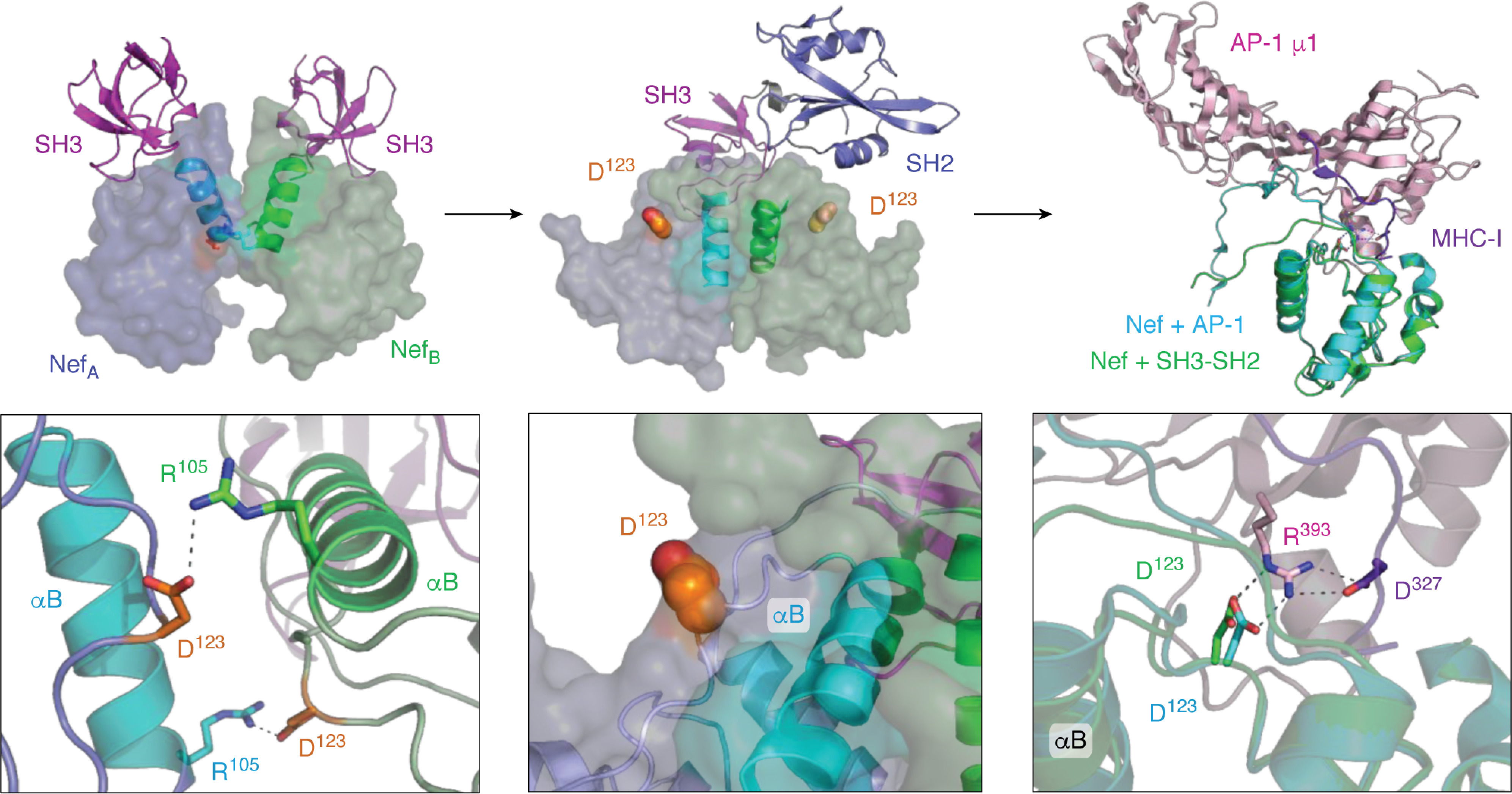
Interaction of HIV-1 Nef with the Src-family kinase Hck may induce conformational changes consistent with MHC-I/AP-1 recruitment. Left, crystal structure of the HIV-1 Nef core in complex with the SH3 domain of Fyn (high-affinity R96I mutant; PDB code 1EFN). Nef forms a dimer of Nef·SH3 complexes in this structure (NefA (blue) and NefB (green)). The dimer interface is formed by the Nef αB helices (highlighted helices). The SH3 domains are shown at the top in pink. The helical dimer interface is enlarged in the bottom panel and highlights the reciprocal polar contacts between Nef Asp-123 and Arg-105, which are buried in the core of this structure. The center, top panel shows the crystal structure of the Nef core in complex with the Hck SH3-SH2 region (PDB code 4U5W). The color scheme is as per the left panel with a single SH3-SH2 unit shown for clarity. Nef also crystallizes as a 2:2 complex of Nef·SH3-SH2 dimers in this structure, but the helical interface is completely reoriented relative to the Nef·SH3 complex such that the Nef Asp-123 side chain (orange) is now pointed toward the solvent. One of the Asp-123 residues is enlarged in the bottom panel. Right, structural alignment of one of the Nef core proteins (green ribbon) in the Nef·SH3-SH2 complex (PDB code 4U5W) with the Nef core (cyan ribbon) in complex with the AP-1/μ1 subunit (pink) and MHC-I tail peptide (purple) from PDB code 4EN2. The Nef core proteins from each complex adopt very similar conformations, with nearly identical positioning of Nef Asp-123 (enlarged in the bottom panel). Nef Asp-123 forms part of an ionic bond network, with Arg-393 from AP-1 and Asp-327 from MHC-I, that is required for Nef-mediated down-regulation of MHC-I and immune escape.
