Figure 4.
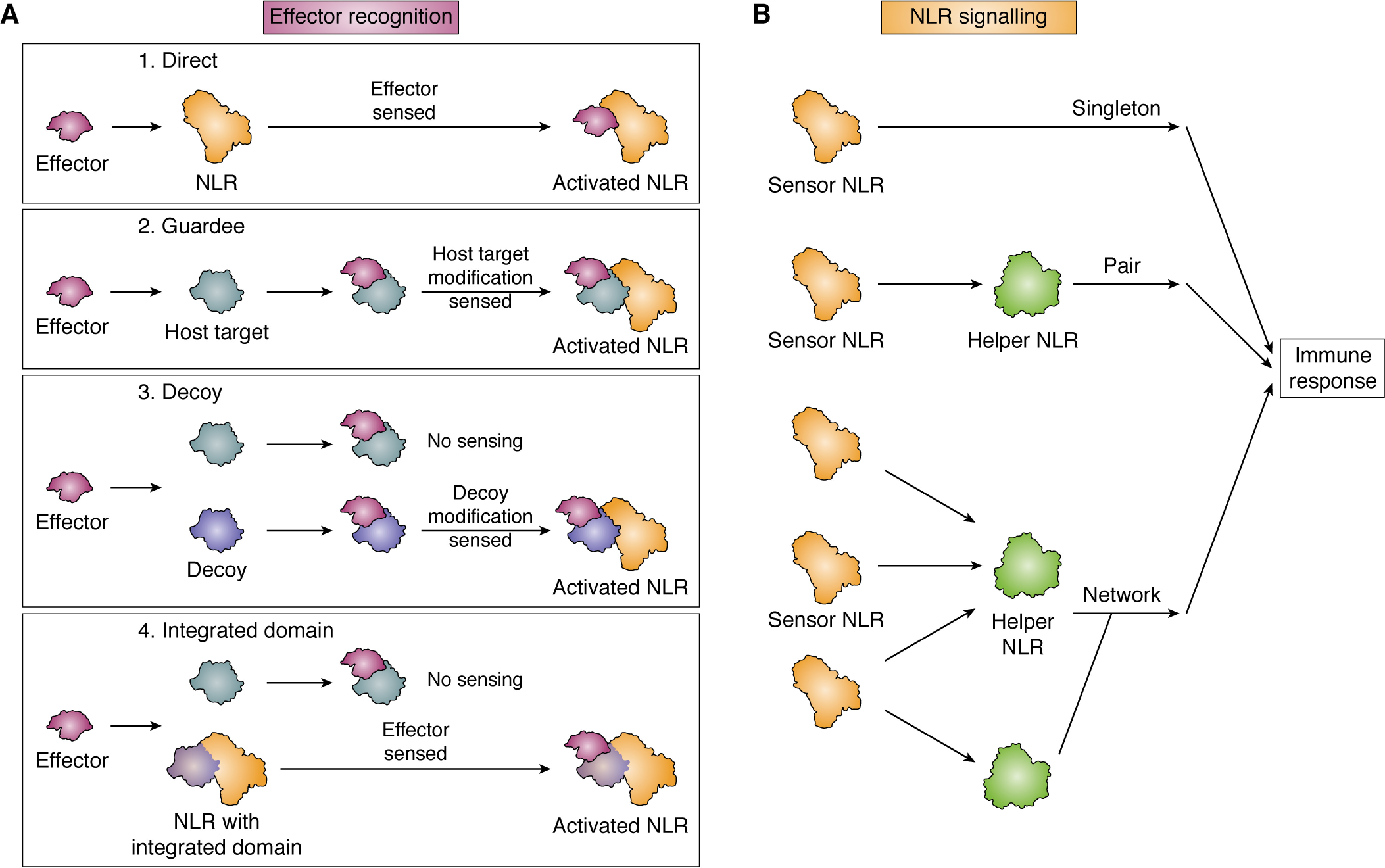
NLRs perceive effectors via distinct mechanisms and induce immune responses through different mechanisms. A, effector (purple) perception induces activation of the NLR (orange) via direct binding. NLRs can indirectly perceive and respond to effectors by monitoring modifications of a physiologically relevant host target (Guardee, gray) or a molecular mimic that likely resulted via gene duplication and is now only involved in immune signaling (Decoy, blue). NLRs can directly perceive and respond to effectors via NLR integrated domains (blue), which likely have their evolutionary origin in ancestral host targets of effectors. B, NLR singletons are able to initiate immune responses upon effector perception. Several sensor NLRs require downstream helper NLRs (green) to transduce effector perception into immune responses. NLRs can function in pairs or as part of interconnected networks.
