Extended Data Fig. 4. Simple spikes promote synchrony whereas complex spikes suppress firing for neighboring cells.
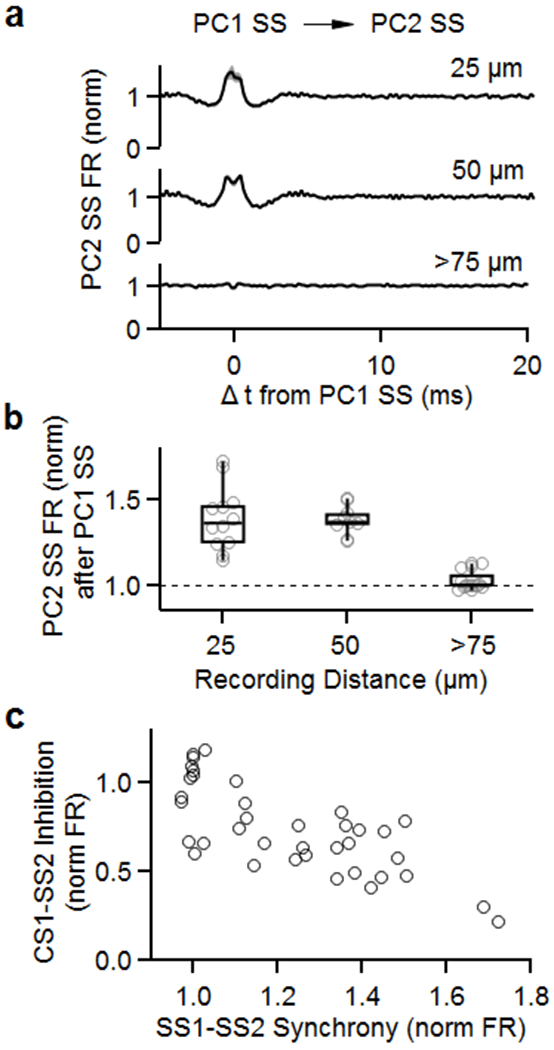
The CC firing of the PC pairs of Fig. 1 were analyzed as described previously 20.
(a) Average firing rate of simple spikes from neighboring PCs (PC2 SS) after simple spikes from PC1 (PC1 SS). Recording sites were separated by 25 μm (top), 50 μm (middle), and more than 75 μm (bottom).
(b) Summary of normalized firing rates of PC2 SS after PC1 SS as a function of distance between recording sites.
(c) Summary of inhibition of PC2 SS by PC1 CS (from Fig. 1) as a function of synchrony between PC1 SS and PC2 SS.
Box plots indicate median and interquartile range with the whiskers indicating the range.
