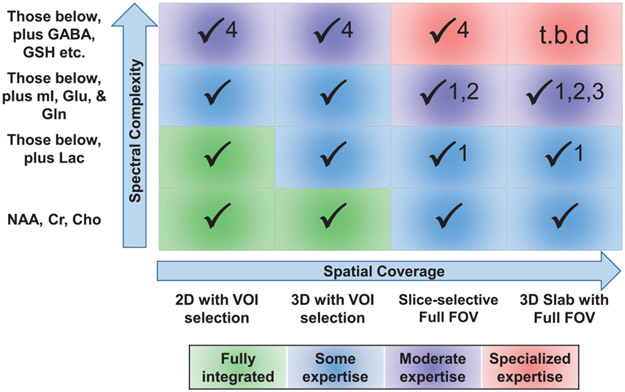
FIGURE 6.
Illustration of the recommended classes of acquisition methods for increasing levels of complexity of the spectral information. The color indicates the level of expertise required, ranging from sequences that are fully integrated into clinical protocols to specialized sequences that require specific research experience. Observations indicated by the numbers are as follows: (1) whole-brain acquisitions are susceptible to increased contamination from extracranial lipids; therefore, results from spectral fitting of lactate are labeled LL (Lipid+Lactate). (2) Whole-slice or whole-brain acquisitions benefit from using higher spatial resolutions92,118,135 and are therefore not optimum for detection of low SNR signal components for ≤3T measurements. (3) Whole-brain acquisitions have large global B0 inhomogeneities and quantitative analysis of resonances close to water and lipid may be impacted in some brain regions. (4) Measurements of compounds that have significant spectral overlap are widely implemented using frequency-spectral editing methods, which are most reliably implemented using volume-selective measurements11,12,209