Extended Data Figure 6.
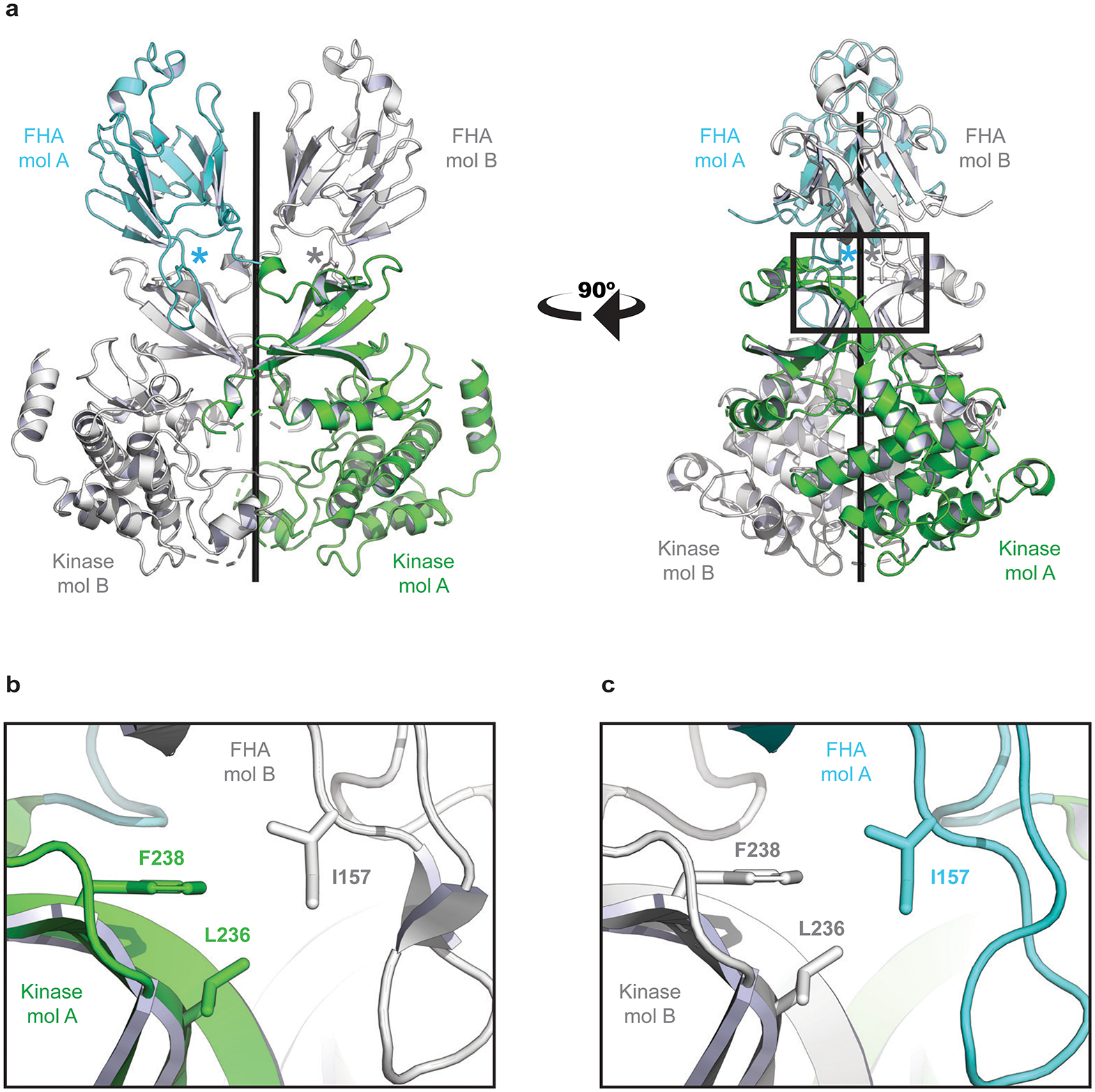
Structural basis for CHK2 homodimer disruption by Isoleucine 157 mutation. a, The crystal structure of the CHK2 (FHA-Kinase) homodimer (PDB: 3I6U). The FHA domain of molecule A (mol A) is shown in cyan and the kinase domain is colored green. A second CHK2 (mol B) has both domains colored white. The two CHK2 molecules are nearly symmetric – coiling around the central axis (black rod). The location of each Isoleucine 157 residue is marked with an asterisk. b, A zoomed window showing details of the interactions. I157 links the FHA of one CHK2 molecule (white) to the kinase domain of a second (green). The side chain of I157 mediates an FHA-Kinase hydrophobic interface, interacting with Phenylalanine 238 (F238) and Leucine 236 (L236) on the kinase domain. c, The second interface of the CHK2 dimer (180° rotation from panel b) is nearly identical. A Threonine at position 157 would diminish these hydrophobic interfaces and destabilize the CHK2 dimer, as has been previously reported.
