Extended Data Figure 4.
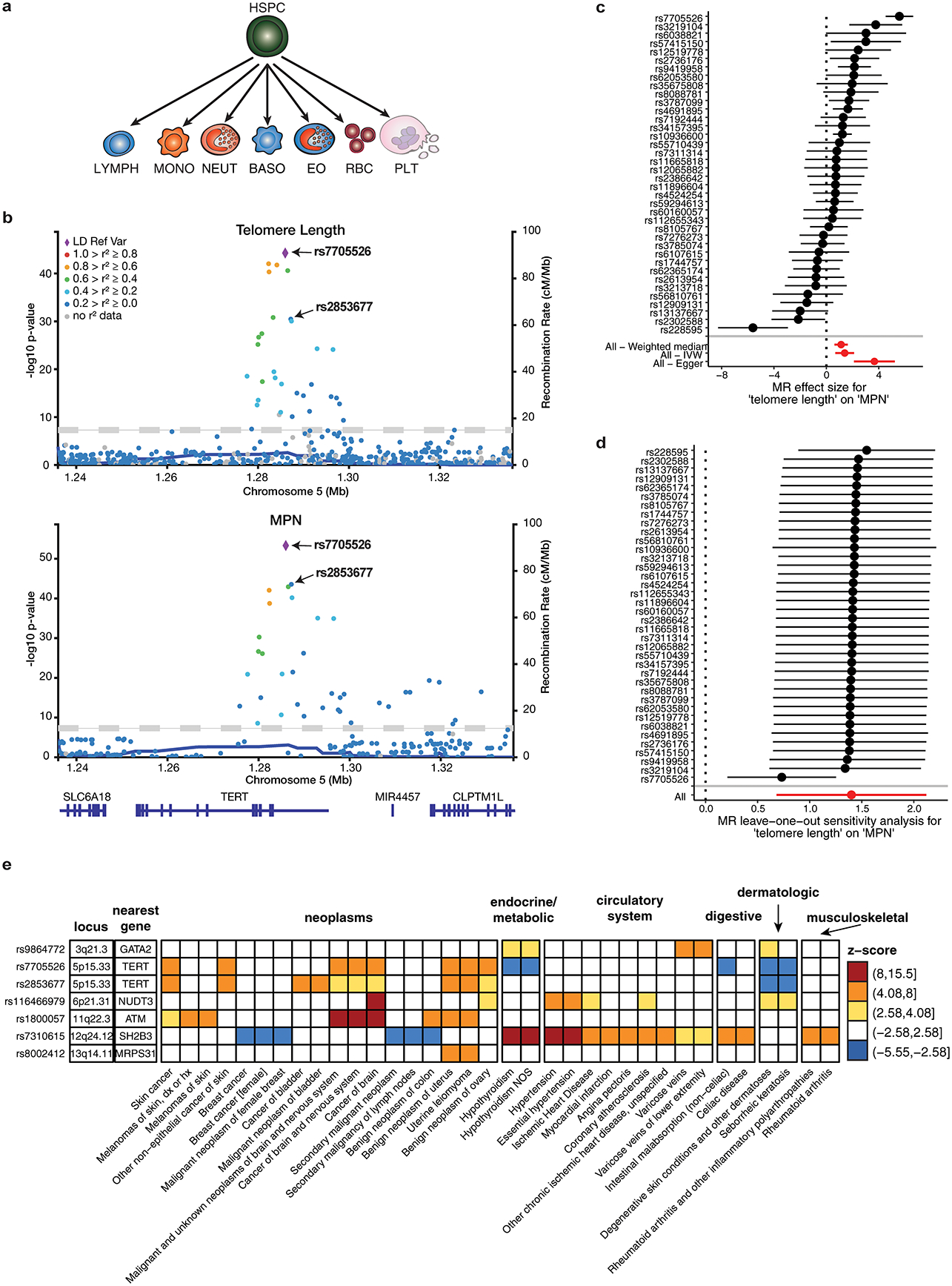
Shared genetic associations between MPN risk and other phenotypes. a, Schematic depicting the trajectory of undifferentiated hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) into various committed cell types: lymphocytes (LYMPH), monocytes (MONO), neutrophils (NEUT), basophils (BASO), eosinophils (EO), red blood cells (RBC), and platelets (PLT). b, Regional association plots at the TERT locus (+/− 50kb from lead variant), showing the associations of variants with leukocyte telomere length and MPN. The colors of the points depict pairwise linkage disequilibrium (r2) to sentinel variant rs7705526. The two conditionally independent lead variants for both traits, rs7705526 and rs2853677, are labeled. c, Individual SNPs associated with telomere length and their effect sizes on MPN risk (n = 2,949 cases and 835,554 controls), calculated using the fixed effects meta-analysis method. Aggregate mendelian randomization (MR) effects, calculated from three different methods (weighted median, inverse-variance weighted, and Egger regression), are shown at the bottom. Data are MR effect sizes and standard errors. Red color indicates significance. d, MR leave-one-out sensitivity analysis, showing MR effect estimates using the inverse variance weighted approach after excluding each individual SNP from the analysis (n = 2,949 cases and 835,554 controls). Data are MR effect sizes and standard errors. e, Phenome-wide association study (pheWAS) of MPN risk variants. We tested fine-mapped MPN risk variants (PP > 0.10 or lead variant) for associations with 1,130 well-represented case-control phenotypes from the UK Biobank, calculated by two-tailed logistic mixed model association test. Shown in this heatmap are the top MPN-associated variants at each locus with one or more associations reaching Bonferroni-corrected significance (p = 0.05 / 1130 phenotypes = 4.4 × 10−5, or abs(z-score) = 4.08). Heatmap color indicates association z-score. All variant effects are oriented with respect to the risk-increasing MPN allele. Phenotypes are divided into major clinical categories, as listed in the annotations above the heatmap.
