Figure 1.
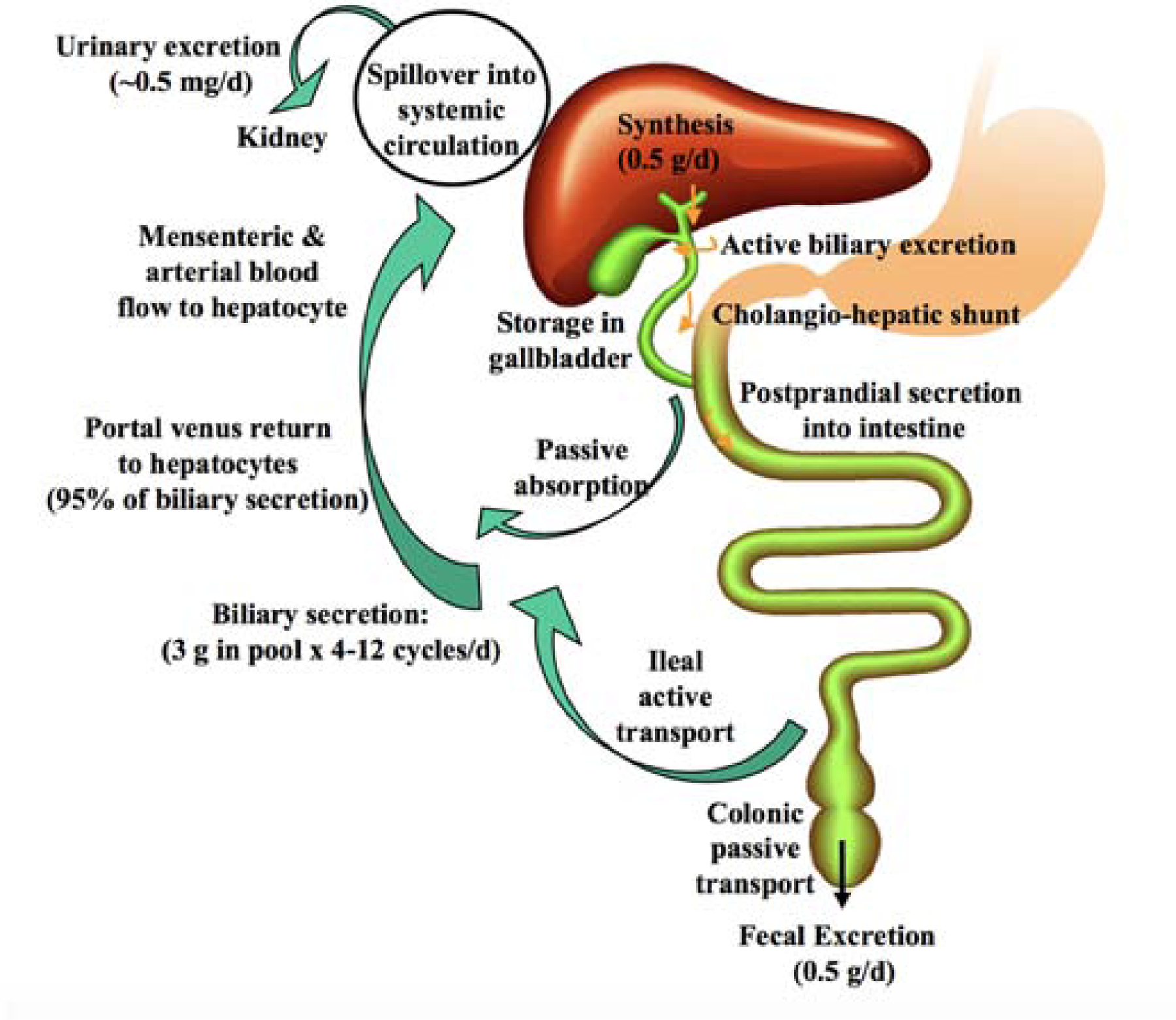
Enterohepatic recycling of bile acids. Bile acids are synthesized in the liver and stored in the gallbladder. At meals, bile acids are excreted to the duodenum for fat emulsification. In small intestine, most bile acids are reabsorbed in the ileum by apical sodium-dependent bile salt transporter (ASBT) and transported back to the liver via portal blood circulation. In this process, about 95% of bile acids are recycled to the liver, and only 5% (~0.5 g) is excreted, which is replenished by the newly synthesized bile acid in the liver. Reproduced, with permission, from reference [58].
