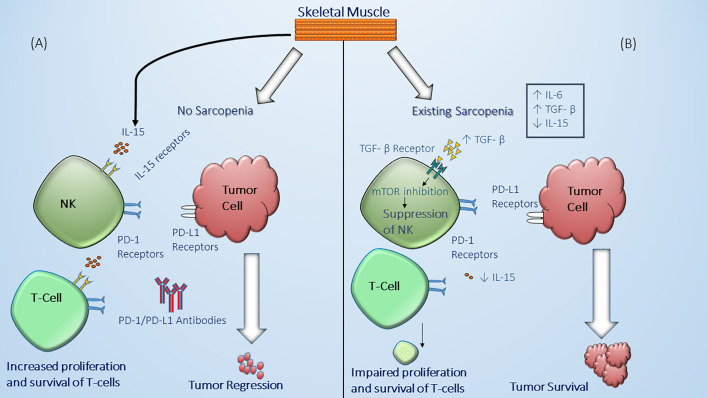
Figure 3.
Effect of sarcopenia on immune system function and anti-tumor mechanisms. (A) in individuals without skeletal muscle wasting (no sarcopenia), there is sufficient production and secretion of IL-15 by skeletal muscle cells which in turn can bind to IL-15 receptors on the natural killer (NK) cell surface and T-cells leading to enhanced functional natural killer cell and proliferation and maintenance of T-cells including CD8+ T-cells against tumor (69). (B) In the presence of significant muscle wasting (sarcopenia), there is decreased production and secretion of IL-15 by skeletal muscle cells (69), as well as an increased chronic inflammatory status in the body associated with high levels of IL-6 and TGF-β (72–74). The latter can lead to NK suppression through mTOR inhibition leading to dysfunctional NK cell which cannot effectively eliminate malignant cells (63, 64, 75). Decreased IL-15 production can lead as well to impaired maintenance, proliferation, and survival of T-cells which are considered potential targets for immune checkpoint inhibitors.