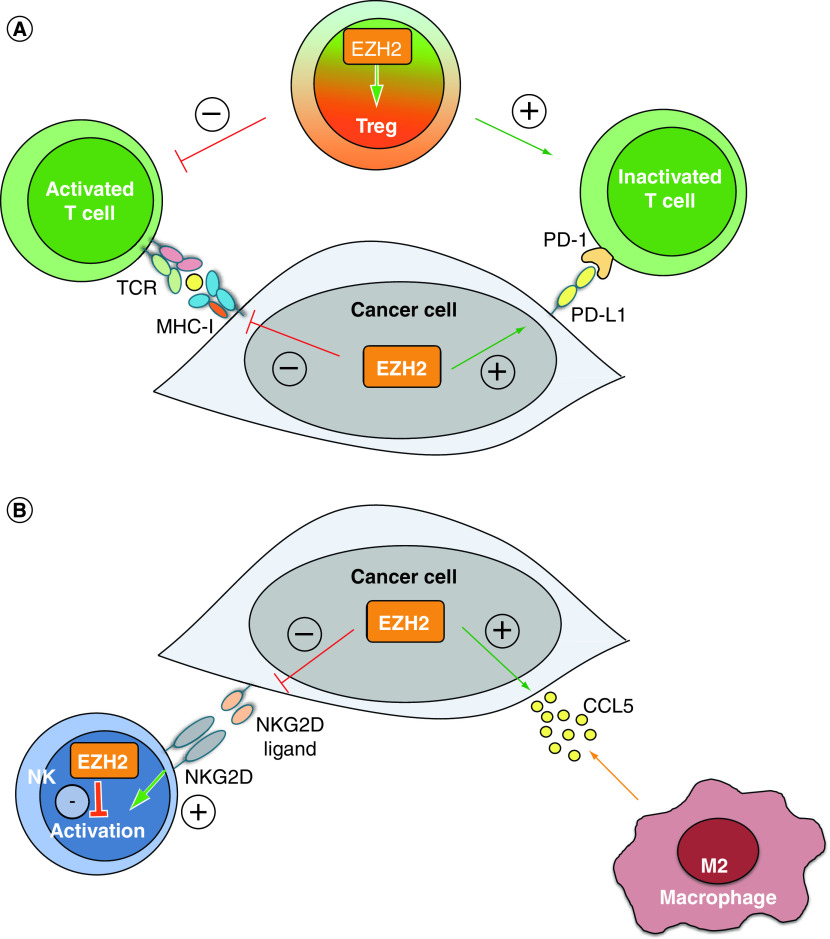
Figure 3. . EZH2 regulates several aspects of the adaptive and innate antitumor immune response.
(A) Intratumoral EZH2 expression suppresses the adaptive antitumor immune response. EZH2 expression in cancer cells inhibits T-cell activation by suppressing the MHC-I antigen presentation pathway and upregulating PD-L1 expression. Besides cancer cells, EZH2 expression in Treg cells is crucial for maintaining their regulatory phenotype and function, which also results in reduced T-cell activation. (B) Intratumoral EZH2 expression suppresses the innate antitumor immune response. EZH2 expression in cancer cells silences the expression of NKG2D ligands, thereby blocking the activation of NK cells and favors the secretion of CCL5, which recruits immunosuppressive M2-type macrophages to TME. Besides cancer cells, EZH2 expression in NK cells directly inhibits their maturation, activation and antitumor activity.
NK: Natural killer.