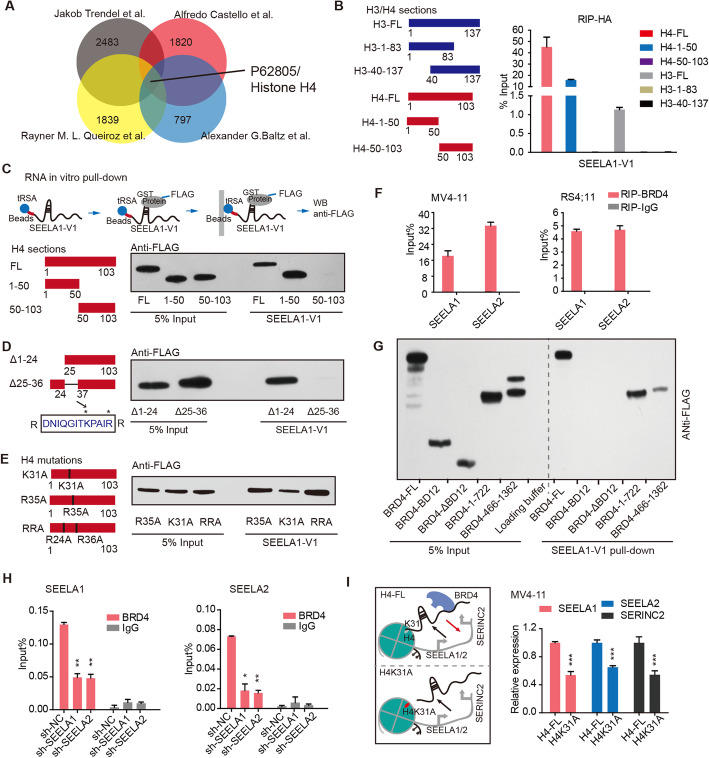
Fig. 3.
SEELA binds K31 aa of histone H4 to promote the enhancer recognition of histone modification reader. a The reported RNA-binding proteomes identified histone H4 (P62805) as a RNA-binding protein candidate. b A schematic diagram shows the truncated fragments of H3 and H4 (left). RIP-qPCR for SEELA1-V1 pull-down by HA-tagged H3 and H4 sections in 293 T cells (right). The anti-HA antibody was used in RIP-qPCR assays. c–e The in vitro tRSA RNA pull-down assay with the purified different mutants of H4 proteins showed that the K31 aa of H4 mainly interacted with SEELA1-V1. f RIP-qPCR detection was used to assess the association of BRD4 with SEELA in MV4-11 and RS4;11 cells. Error bars reflect ± SEM in three independent experiments. An IgG antibody acted as a negative control. g Immunoblot detection of Flag-tagged BRD4 truncated fragments retrieved by in vitro-transcribed tRSA-tagged SEELA1-V1 from 293 T cell lysates. BRD4 (aa 1-1362, aa 1-722, and aa 466-1362) presented significantly higher enrichment of SEELA1-V1. h ChIP-qPCR assays after knocking down SEELA showed that the enrichments of BRD4 at the SEELA locus were downregulated in MV4-11. Error bars reflect ±SEM (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01) in three independent experiments. An IgG antibody was used as a negative control in the ChIP assay. i A schematic diagram (left) shows stable overexpressed HA-tagged H4-full length or H4K31A into MV4-11 cells. The binding of SEELA is disrupted in H4K31A mutants, as a result, the missing of the SEELA-induced SERINC2 expression. The expression of SEELA and SERINC2 (right) were downregulated in H4K31A mutant expression cells versus that in the H4-full length expression cells. Error bars reflect ± SD (***P < 0.001) in three independent experiments