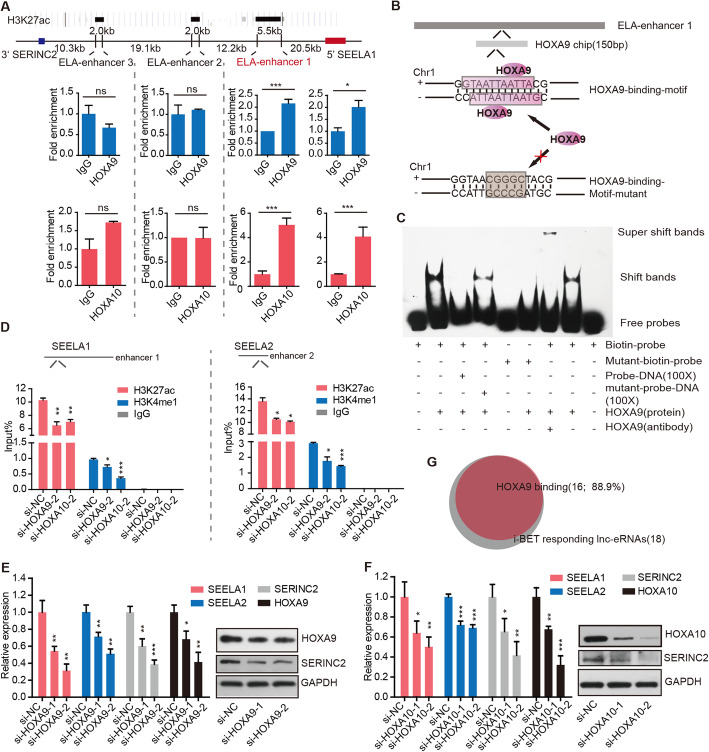
Fig. 5.
HOXA9/HOXA10 binds to the upstream enhancer of SEELA to reprogram the enhancer-related histone mark. a A schematic diagram shows the genomic location and the H3K27ac enrichment of ELA-enhancer 1/2/3 (located at the region 20.5 kb, 38.2 kb, and 59.3 kb upstream of SEELA1, respectively). ChIP-qPCR assays of HOXA9 (middle) and HOXA10 (bottom) showed that HOXA9/HOXA10 bound to ELA-enhancer 1 instead of ELA-enhancer 2/3; Error bars reflect ± SD (*P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; ns, no significant) in three independent experiments. An IgG antibody was used as negative controls in the ChIP assay. b, c A schematic diagram shows the normal and mutant DNA sequences that are predicted in HOXA9 located (b). EMSA experiments validated the binding motif of HOXA9/10, which was a 14 bp motif (GGTAATTAATTACG) (c). d ChIP-qPCR assay results of H3K27ac and H3K4me1 after knocking down HOXA9 and HOXA10, the enrichment of enhancer histone marks in the SEELA locus were decreased. Error bars reflect ± SEM (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001) in three independent experiments. An IgG antibody was used as a negative control in the ChIP assay. e, f qPCR and western blotting showed that the mRNA and protein levels of SEELA and SERINC2 were reduced after knocking down HOXA9 (e) or HOXA10 (f). Error bars reflect ± SD (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001) in three independent experiments. g Analysis of the chip-seq data showed that 16 of 18 i-BET responding lnc-eRNAs loci were marked by HOXA9