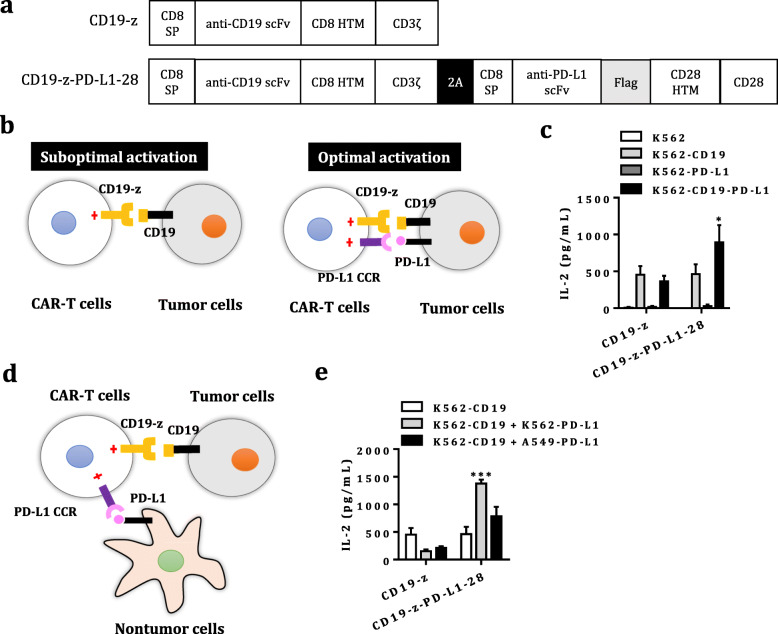
Fig. 1.
Design and characterization of the PD-L1 CCR in Jurkat T cells. a Schematic representation of the CD19 CAR and PD-L1 CCR constructs. The CD19 CAR (CD19-z) was generated by using the first-generation CAR that contains the CD19-targeting scFv fused to the human CD8 hinger and transmembrane domain, followed by the CD3ζsignaling domain. CD19-z-PD-L1–28 was generated by linking CD19-z to the PD-L1 CCR that generated by fusing a humanized PD-L1-binding scFv to the hinger, transmembrane and human CD28 costimulatory domain, via the self-cleaving T2A peptide sequence. b The first-generation CAR-engineered T cells achieve suboptimal activation when exposed to a single target antigen but are fully activated by tumor cells expressing target antigen and PD-L1 through coexpression of the PD-L1 CCR, providing a costimulatory signal. c The levels of IL-2 in the supernatant secreted by CD19-z- and CD19-z-PD-L1–28-engineered Jurkat T cells in the 24 h co-culture system (E:T, 1:1) were measured by ELISA. The results are presented as the mean ± SEM of seven independent experiments, * P < 0.05 with respect to co-culture with CD19+ K562 cells, analyzed using Student’s t-test. d Dual-targeted CAR-T cells can be stimulated with PD-L1+ host cells (e.g., macrophages, dendritic cells) when exposed to PD-L−tumor cells expressing CAR-targeted antigen. e The levels of IL-2 released by CD19-z and CD19-z-PD-L1–28-engineered Jurkat T cells were measured by ELISA after 24 h of incubation at an E:T:host cell ratio of 3:1:1. The results are reported as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, *** P < 0.001 with respect to co-culture with CD19+ K562 cells, analyzed using Student’s t-test