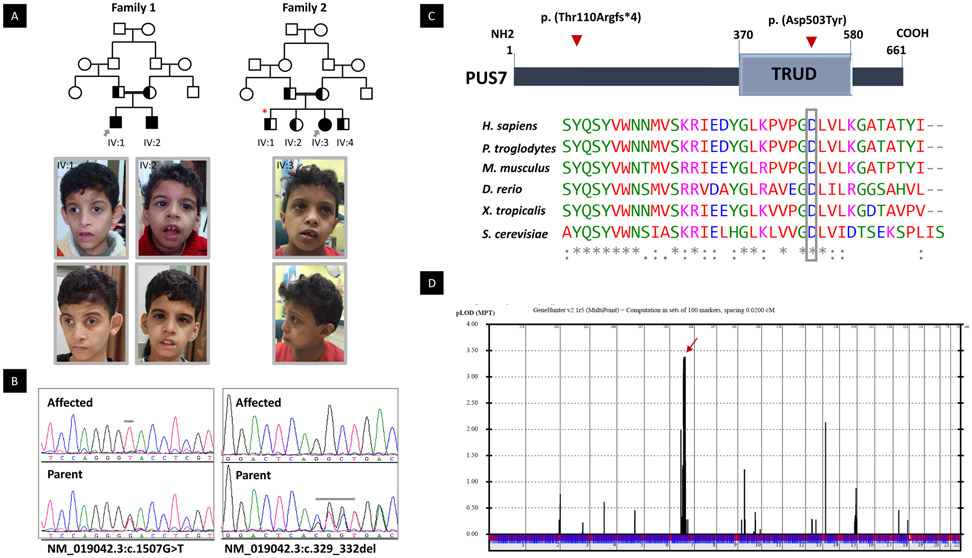
Figure 1:
PUS7 Mutations Cause Intellectual Disability and Microcephaly. A) upper panel: Families pedigrees of 12DG2083 & 12DG2084 (Family 1) and 16DG0965 (family 2) showing the consanguineous nature of the parents. The index is indicated in each pedigree by grey arrow, and segregation analysis denoted by half black color (carrier). Red star denotes sibling with resolved hydrocephalus. Lower panel the facial photos of the affected individuals in this study. IV:1 (12DG2083) at the age 9 years and 16 years old. Note Triangular face, prominent glabella, arched eyebrows, deep set eyes, infraorbital crease, convergent squint, hypoplastc zygomatic arches, anteverted nostrils and prominent ears with simple helix. IV:2 (12DG2083) at the age of 7 and 14 years old. Note the deep-set eyes and infraorbital crease, downward slanting of eyes low set ears and thick lower lip. IV:3 (16DG0965) at the age of 8 years. Note the microcephaly, of mildly upturned nares and everted lower lip. B) Sequence chromatograms showing the homozygous variants in PUS7 in the index of each family and the heterozygous in the parents. C) Upper panel is the schematic of PUS7 showing the position of domain” TRUD” and the location of the two variants p. (Thr110Argfs*4) and p. (Asp503Tyr). Lower panel showing multisequence alignment of the mutated reside p. (Asp503) showing high conservation down to S. cerevisiae (boxed in gey). D) Genome-wide linkage analysis to the two families revealed a single maximal peak with a LOD score of ~3.4 on chromosome 7.