Figure 1.
ZIKV Can Be Transmitted via Corneal Transplantation in AG129 Mice but Infects Human Corneal Explants Inefficiently
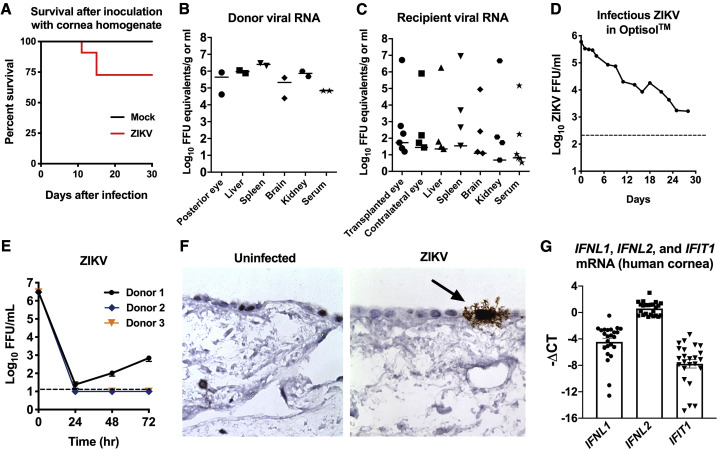
(A) Survival of AG129 mice inoculated with Ifnar1−/− corneal homogenates 7 days after subcutaneous inoculation with ZIKV (n = 11) or uninfected Ifnar1−/− cornea control homogenates (n = 4).
(B and C) ZIKV mRNA expression in tissues was quantitated using qRT-PCR. Tissues were harvested from cornea donors (n = 2) and recipient (n = 6) mice on days 6 and 7 after infection.
(D) ZIKV (6 × 105 FFU) was stored in cornea storage medium (Optisol) at 4°C for 28 days. Infectious virus was measured by focus forming assay at the indicated time points.
(E) Human donor corneas (n = 4 technical replicates per donor from three independent donor corneas) were inoculated with 3 × 106 FFU/mL of ZIKV (Brazil strain), and infectious virus was quantitated at the indicated time points by focus forming assay. Data represent the mean ± SEM.
(F) RNA ISH and histological analysis was performed on uninfected (left panel) and ZIKV-infected (right panel) human corneal explants in order to determine virus tropism. The black arrow indicates infected corneal epithelial cells.
(G) Baseline expression of IFNL1, IFNL2, and IFIT1 was measured using qRT-PCR in three human donor corneas in independent experiments. Data represent the mean ΔCT ± SEM relative to expression of GAPDH. Each cornea was sectioned to produce eight technical replicates per experiment (n = 24) from three biological replicates in independent experiments.