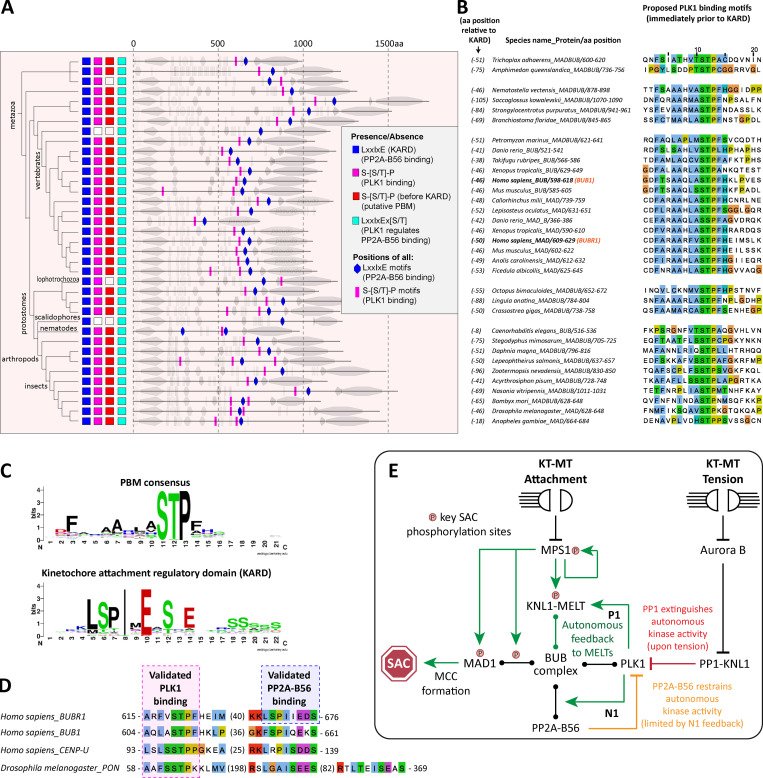
Figure 5.
Evolution of PBMs and PP2A-B56 binding motifs (KARD) in MADBUB homologues. (A) Annotation of PBMs (Ser-Ser/Thr-Pro) and PP2A-B56 binding motifs (LxxIxE, KARD) positions within metazoan MADBUB homologues that contain a KARD. Adapted from Tromer et al. (2016); see Fig. S8 and Data S1 for complete list of 152 eukaryotic MADBUB homologues. (B) Alignment of proposed PBM (located immediately before the KARD) in the species represented in A. (C) Consensus sequence of PBMs listed in B (for consensus motif of other PBMs within eukaryotic MADBUB homologues, see Fig. S9) and the KARD within all eukaryotic MADBUB homologues. (D) Alignment of PBM and KARD in BUBR1, BUB1, PON, and CENP-U. Note: PON is a Drosophila gene with no known homologues in humans, which is involved in mitotic asymmetric division during Drosophila brain development (Lu et al., 1998). (E) Schematic model to illustrate relevant feedback loops involved in SAC activation and silencing (see Results and discussion for explanations). KT-MT, kinetochore-microtubule.