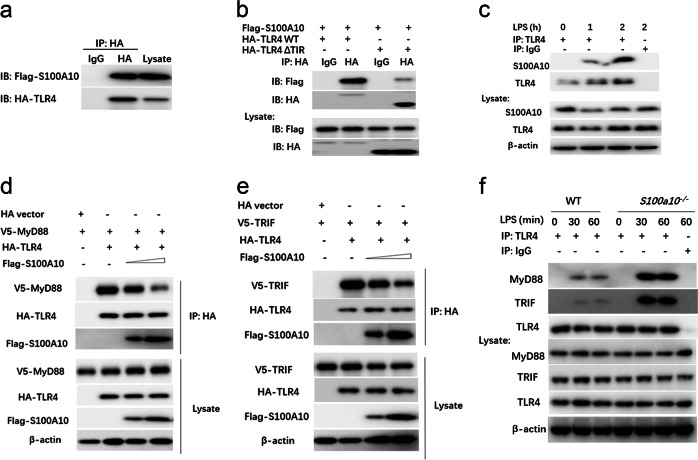
Fig. 6.
S100A10 interacts with TLR4 and affects its association with adaptor proteins. a HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with expression plasmids for Flag-tagged S100A10 and HA-tagged TLR4 as indicated. Twenty-four hours later, cell lysates were prepared and immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-HA or control IgG. The precipitates and whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot (IB) with antibodies for the indicated antigens. b HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with plasmids expressing Flag-tagged S100A10 and either HA-tagged full-length TLR4 (HA-TLR4 WT) or HA-tagged truncated TLR4 lacking TIR (HA-TLR4-ΔTIR); IP with anti-HA or control IgG was followed by IB with anti-Flag and anti-HA antibodies. c Bone marrow-derived macrophages from WT (n = 3) mice were stimulated with LPS for the indicated time periods. Cell lysates were then subjected to IP with anti-TLR4 or control IgG, followed by IB analysis with anti-S100A10, anti-TLR4, and anti-β-actin antibodies. d, e HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with plasmids expressing HA-tagged TLR4 or HA-tagged empty vector, V5-tagged MyD88 (d) or V5-tagged TRIF (e) together with increasing amounts of Flag-tagged S100A10; IP with anti-HA was followed by IB with anti-Flag, anti-V5, anti-HA, and anti-β-actin antibodies. f Bone marrow-derived macrophages from WT and S100a10−/− mice (n = 3 per group) were treated with or without LPS (100 ng/ml) for the indicated times. Cell lysates were then subjected to IP with anti-TLR4 or control IgG, followed by IB analysis with anti-TLR4, anti-MyD88, anti-TRIF, and anti-β-actin antibodies. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments