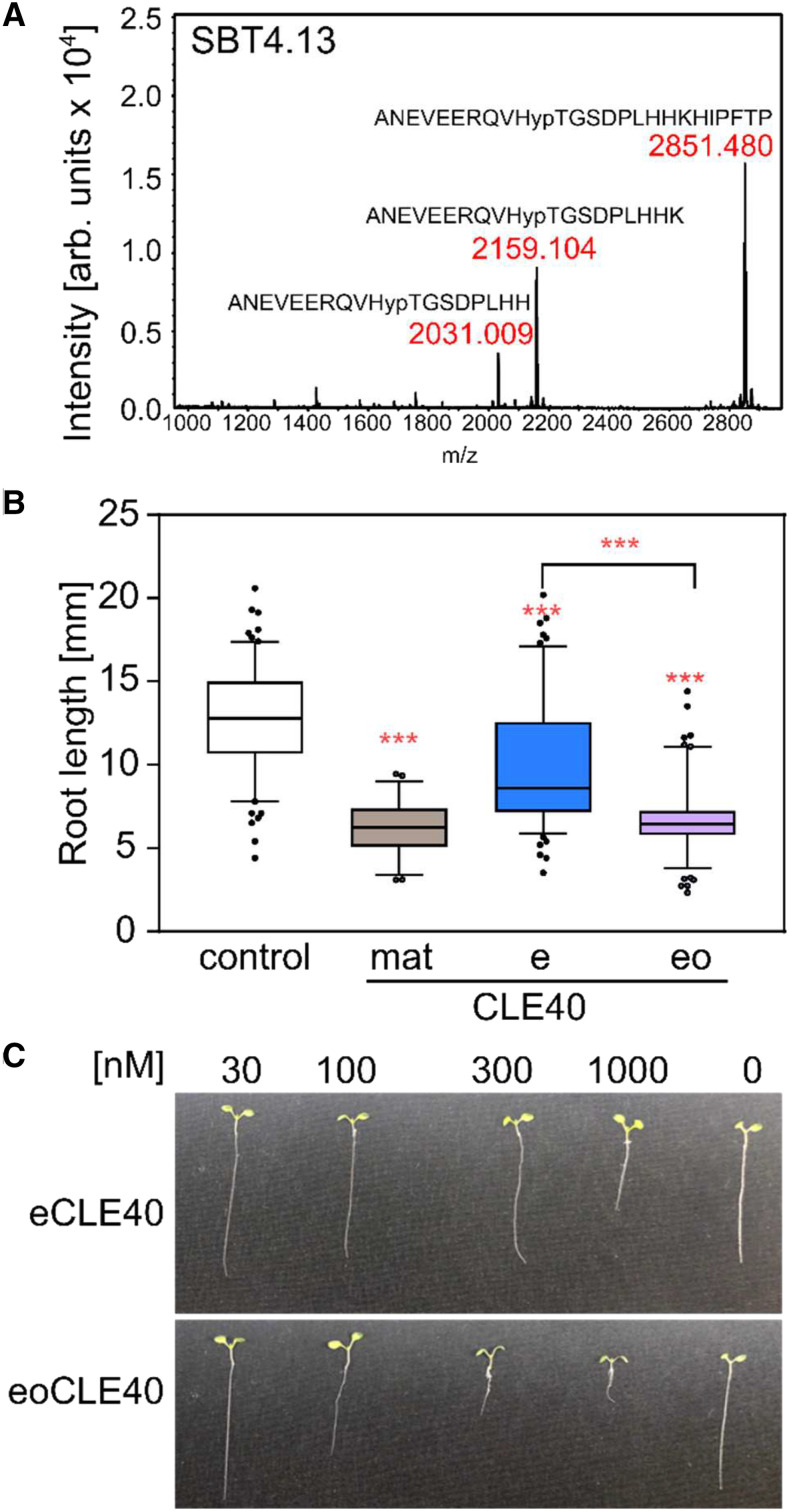
Figure 7.
Relevance of Pro hydroxylation for CLE40 precursor peptide processing and activity. A, Cleavage of the extended CLE40 peptide by SBT4.13 (compare with Fig. 3A) is prevented by hydroxylation of P4. eoCLE40 was digested with affinity-purified SBT4.13 (control reaction in Supplemental Fig. S3B). Reaction products were analyzed by MALDI-TOF MS. The mass spectrum shows ion intensities (arbitrary units) and masses for the substrate peptide (m/z = 2,851.480) and two C-terminally processed cleavage products. B and C, Hydroxylation at P4 is required for full activity of the extended CLE40 peptide. Bioactivity (root growth inhibition) was assayed in seedlings grown for 5 d on plates containing 1 µm matCLE40, eCLE40, eoCLE40, or no peptide as a control. B, Root length of peptide-treated as compared with control seedlings (means ± se; n ≥ 49). Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences of peptide-treated roots and the control, and between eCLE40- and eoCLE40-treated roots using Student’s t test (***P < 0.001). C, Representative seedlings treated with the indicated concentrations of eCLE40 or eoCLE40 as described for B.