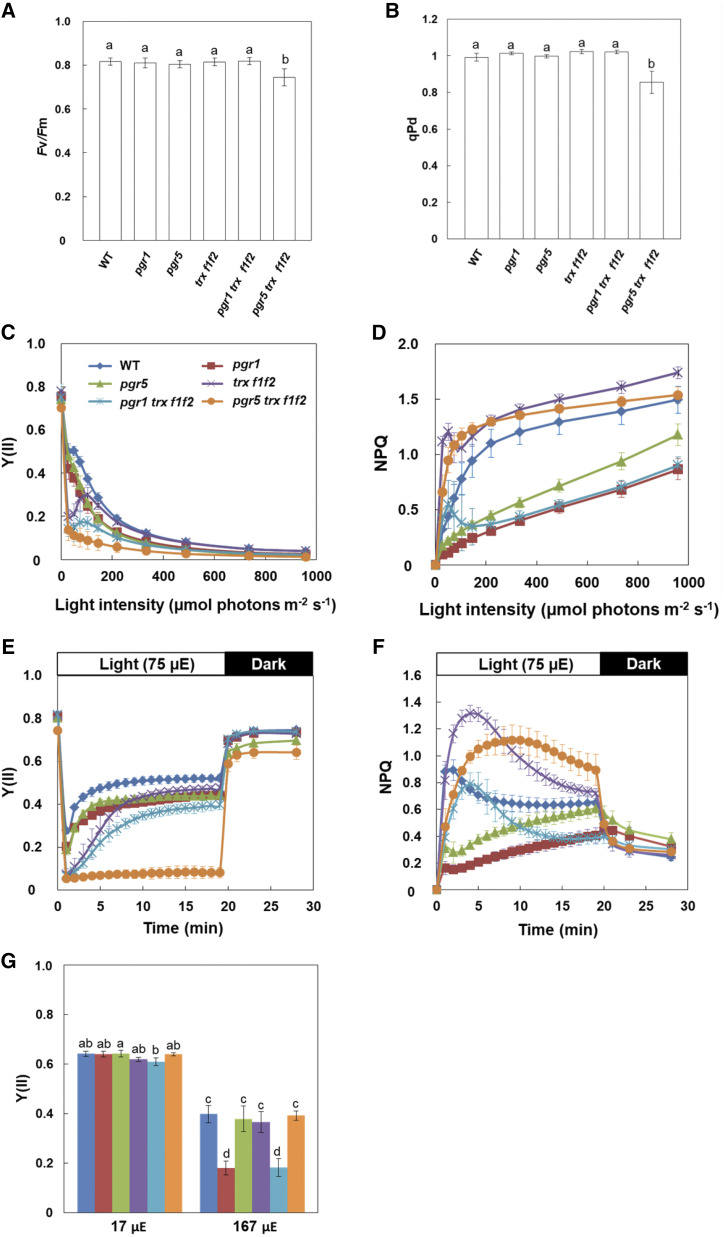
Figure 2.
Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis in the wild type (WT) and pgr1, pgr5, trx f1f2, pgr1 trx f1f2, and pgr5 trx f1f2 mutants. A, The Fv/Fm. B, qPd. qPd was determined after illumination at 50 μmol photons m−2 s−1 (growth light) for 15 min. Each value is the mean ± sd of five independent replicates. Columns with the same letters are not significantly different between genotypes by Tukey-Kramer test (P < 0.05). C and D, Light intensity dependence of the Y(II) and the NPQ of chlorophyll fluorescence. Each value is the mean ± sd of five independent replicates. E and F, Time courses of Y(II) and NPQ during the induction of photosynthesis. The Y(II) and NPQ values were measured upon illumination at 75 µmol photons m−2 s−1 for 20 min, followed by 8 min in the dark. Each data point represents the mean ± sd (n = 5 independent plants). G, Linear electron transport in ruptured chloroplasts. Y(II) was determined in ruptured chloroplasts at light intensities of 17 and 167 µmol photons m−2 s−1 (µE). Each value is the mean ± sd of three independent chloroplast preparations. Columns with the same letters are not significantly different between genotypes by Tukey-Kramer test (P < 0.05).