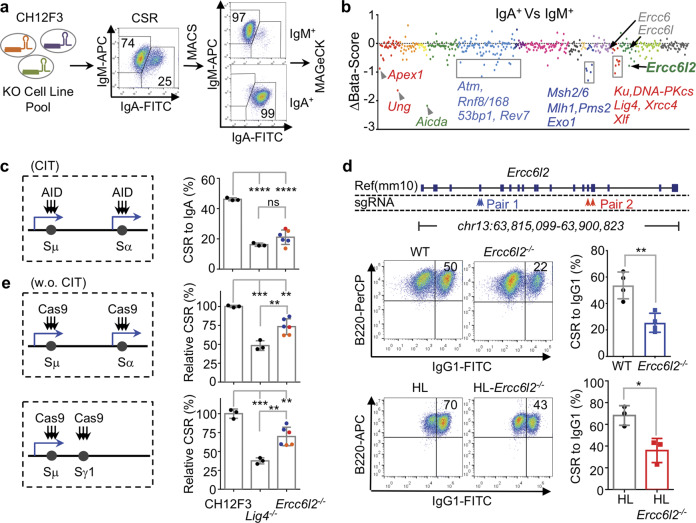
Fig. 2. ERCC6L2 is required for optimal CSR.
a Schematic illustration of CSR screening procedure. Representative flow cytometry plots are showed. b Enriched CSR genes. Genes are grouped and illustrated as Fig. 1d. The beta-score difference (IgA+–IgM+) is plotted and representative genes are labeled. c ERCC6L2 is required for optimal CSR in CH12F3 cells. AID-initiated CSR is illustrated at left, and CSR to IgA in presence of cytokines (CIT, α-CD40/IL4/TGFβ) of indicated cells are plotted at right. Blue arrows indicate transcription. Colored points indicate knockout clones obtained with different sets of sgRNAs. d ERCC6L2 is required for optimal CSR in ex vivo activated splenic B cells. Gene knockout strategies with two sets of sgRNAs are illustrated on top. Representative CSR flow cytometry plots are showed at left. Data from four pairs of Ercc6l2−/− (sgRNA Pair 1) and wild-type (WT) mice and three pairs of HL-Ercc6l2−/− (sgRNA Pair 2) and corresponding Ig heavy and light chain knockin (HL) mice are summarized. e ERCC6L2 is required for optimal Cas-CSR. CRISPR/Cas9-initiated CSR is schematically illustrated at left, and normalized CSR level of indicated cells are plotted at right. Data are represented as mean ± SD (standard deviation) in (c, d, e). Two-tail unpaired t-test was performed for (c, d, e). ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05; ns: p > 0.05.