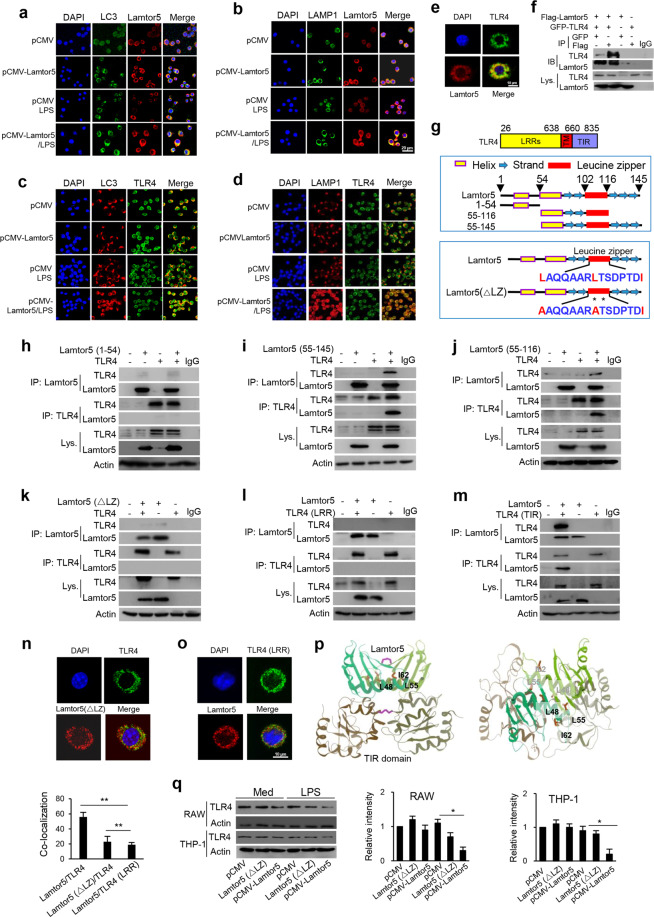
Fig. 5.
Lamtor5 interacts with TLR4 and promotes its tethering at autolysosomes upon LPS stimulation. a, b Colocalization of Lamtor5 with LC3 or LAMP1 and c, d colocalization of TLR4 with LC3 or LAMP1 in control and Lamtor5-expressing RAW264.7 cells stimulated with LPS for 1 h. e Colocalization of TLR4 with Lamtor5 in RAW264.7 cells stimulated by LPS for 1 h. f Coimmunoprecipitation of Lamtor5 and TLR4 in 293T cells transfected with control, GFP-TLR4- and/or Flag-Lamtor5-expressing plasmids. IgG was used as a control. g Schematic illustration of the TLR4 structure and truncated TLR4 fragments (upper), the Lamtor5 structure and truncated Lamtor5 fragments (middle), and the LZ-mutant fragment (lower). h–k Coimmunoprecipitation of Lamtor5 and TLR4 in 293T cells transfected with plasmids harboring intact Lamtor5- or truncated/mutant Lamtor5-expressing plasmids with or without TLR4-expressing plasmids; l, m Coimmunoprecipitation of Lamtor5 and TLR4 in 293T cells transfected with plasmids encoding truncated TLR4 constructs and/or Lamtor5. n, o Colocalization of TLR4 with Lamtor5 in 293T cells transfected with intact Lamtor5- or mutant Lamtor5-expressing plasmid with or without TLR4-expressing plasmid. p Stereoview of the interaction between TLR4 (TIR) and Lamtor5 fragments using the I-TASSER server. Both TLR4 (TIR) and the Lamtor5 fragments are modeled as dimers, and the leucine zipper (LZ) structure at the interactive interface is shown. q Immunoblotting for TLR4 in RAW264.7 or THP-1 cells transfected with Lamtor5- or Lamtor5 (ΔLZ)-expressing plasmids. Quantified relative band intensities are also shown. Representative images are shown, and the data from three independent experiments are expressed as the means ± SDs. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 by Student’s t-test