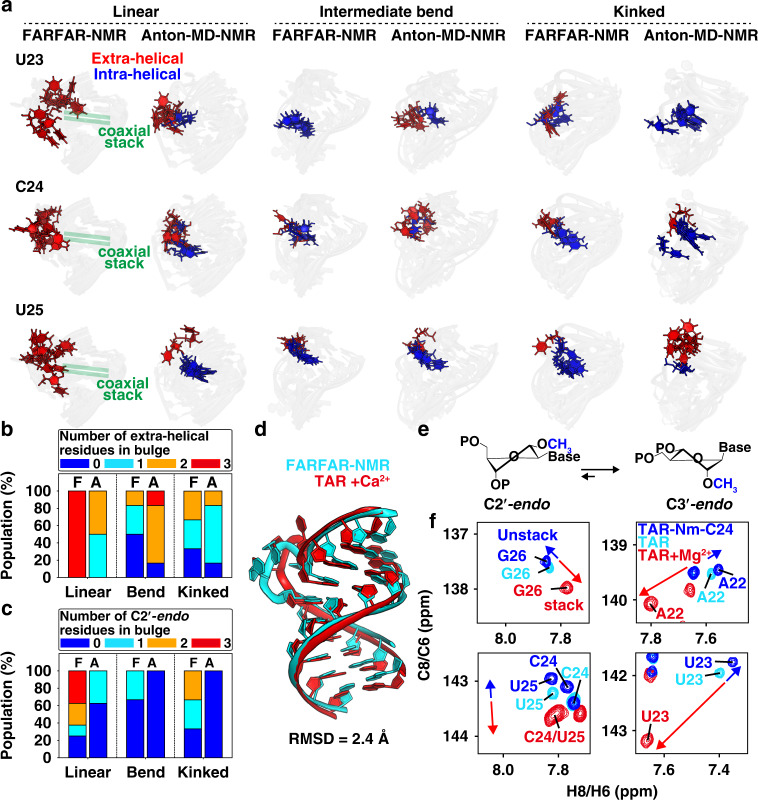
Fig. 5. Cooperative extra-helical flipping and sugar repuckering of bulge residues are coupled to coaxial stacking.
a Overlay of conformers showing motions in bulge residues for linear (|βh| < 45°), intermediate bend (45° < |βh| < 70°) and kinked (|βh| > 70°) inter-helical conformations in the FARFAR-NMR and Anton-MD-NMR ensembles. b, c The fractional populations of conformers with the number of b extra-helical and c C2′-endo residues (color-coded) in the bulge residues (U23, C24, and U25) as a function of bending angle in the FARFAR-NMR (“F”) and Anton-MD-NMR (“A”) ensembles (N = 20). d Comparison of one coaxially stacked FARFAR-NMR conformer with the crystal structure of Ca2+-bound TAR (PDBID: 397D)33. e Nm shifts sugar-pucker equilibrium towards C3′-endo. f Overlay of 2D [13C, 1H] HSQC NMR spectra of the aromatic spins for TAR-Nm-C24 without Mg2+ (blue) with blue arrows indicate unstacking, TAR without Mg2+ (cyan) and TAR with 3 mM Mg2+ (red) with red arrows indicating increased coaxial stacking.