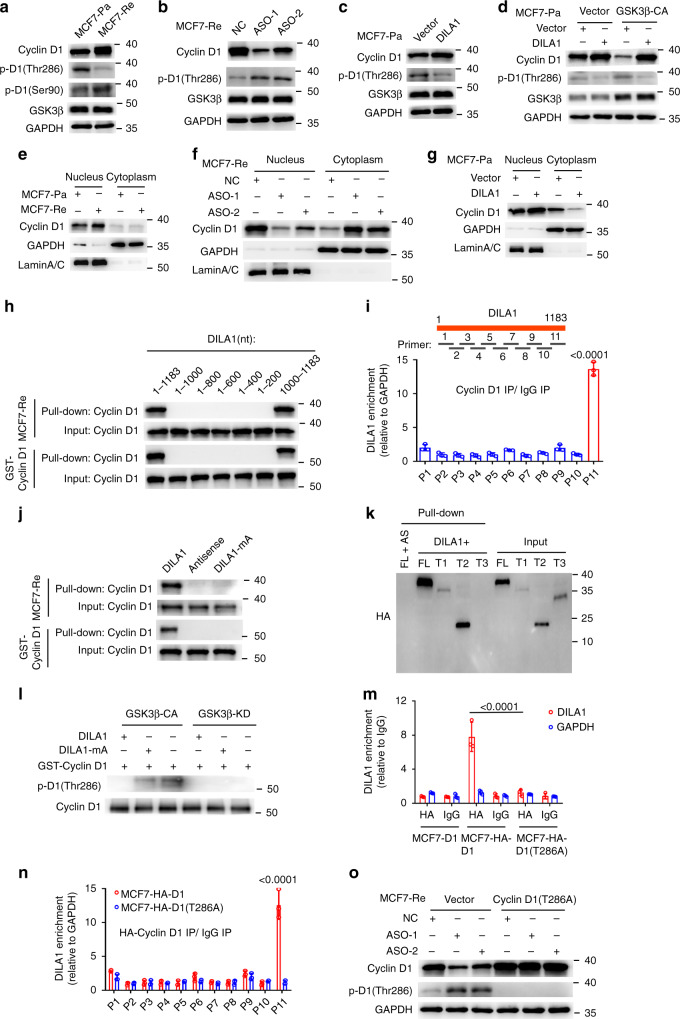
Fig. 4. Hairpin A of DILA1 interacts with Thr286 of Cyclin D1 and inhibits its phosphorylation and nuclear-to-cytoplasmic redistribution.
a Western blotting showing the levels of Cyclin D1, phosphorylated Cyclin D1 (p-D1) (Thr286), p-D1 (Ser-90), and GSK3β in MCF7-Pa and MCF-Re cells. b–d Western blotting showing the levels of Cyclin D1, p-D1(Thr286), and GSK3β in DILA1-silenced MCF-Re cells (b), in DILA1-overexpressed MCF7-Pa cells (c), and in DILA1 and constitutively activated GSK3β (GSK3β-CA) both overexpressing MCF7-Pa cells (d). GAPDH was used as a loading control. e–g Western blotting showing the levels of nuclear and cytoplasmic Cyclin D1 in MCF7-Pa and MCF-Re cells (e), in DILA1-silenced MCF-Re cells (f), and in DILA1-overexpressed MCF7-Pa cells (g). GAPDH and Lamin A/C was used as cytoplasmic and nuclear controls, respectively. h RNA pull-down showing the interaction between Cyclin D1 and full-length or serial truncation mutants of DILA1. i eCLIP-qPCR assay indicating the exact DILA1 region responsible for Cyclin D1 binding in MCF7-Re cells (bottom). A schematic diagram of DILA1 primers (P1–P11) designed for eCLIP-qPCR, covering the full length of DILA1 (top). j RNA pull-down showing the interaction between Cyclin D1 and DILA1 or DILA mutant with deletion of hairpin A (DILA1-mA). k RNA pull-down showing the interaction between DILA1 and HA-tagged full length or truncation mutants (FL (1–295), T1 (20–295), T2 (91–295), and T3 (1–256)) of Cyclin D1 proteins in MCF-7 cells. AS (antisense) was used as a negative control. l In vitro kinase assay showing the phosphorylation of Cyclin D1 at Thr286 by active GSK3β-CA or inactive GSK3β-KD in the absence or presence of DILA1 or DILA1-mA. m RIP-qPCR of DILA1 immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody or IgG in MCF7-Re cells with ectopically expressed HA-Cyclin D1 or HA-Cyclin D1(T286A). n eCLIP-qPCR assay in MCF7-Re cells with HA-Cyclin D1 or HA-Cyclin D1(T286A) overexpressed. For i, m, n, n = 3 biologically independent experiments, means ± s.d. are shown, and p values were determined by two-tailed Student’s test. o Western blotting showing the levels of Cyclin D1 and p-D1(Thr286) in MCF7-Re cells transfected with control vector or vector expressing Cyclin D1(T286A) and then transfected with NC or DILA1-ASOs. For a–h, j–l, o, representative images of three biologically independent experiments are shown.