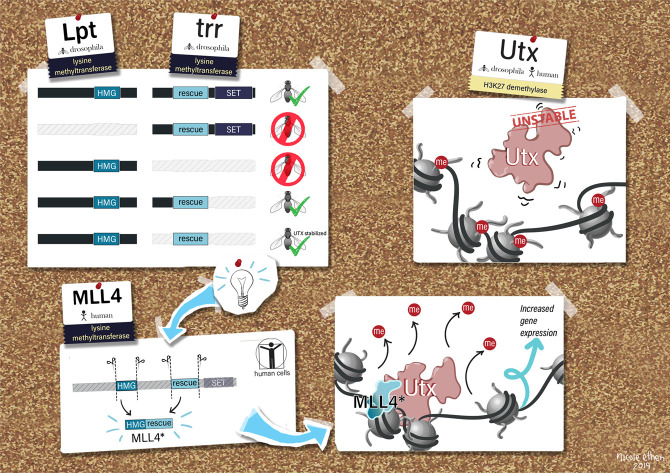
Figure 5.
Model for trr/MLL3/4-mediated UTX stabilization and function at chromatin. Lpt and Trr represent a gene split, corresponding to the N-terminal and C-terminal halves of MLL4, respectively, and both are required for Drosophila viability. We mapped an ∼600-amino-acid region of Trr, corresponding to ∼25% of the full-length protein, which is able to rescue Trr-null lethality. While this region does not overlap any known domains, we demonstrate its ability to bind and stabilize Utx both in flies and human cells. The HMG domain of Lpt was previously reported to associate with Trr by coimmunoprecipitation, suggesting that Lpt may also play a role in mediating Utx stability in Drosophila. We found that in the absence of MLL3/4, UTX stabilization is achieved by expressing a minimal UTX-interacting peptide fused to MLL4's HMG domain.