Fig. 1. The scLearn workflow.
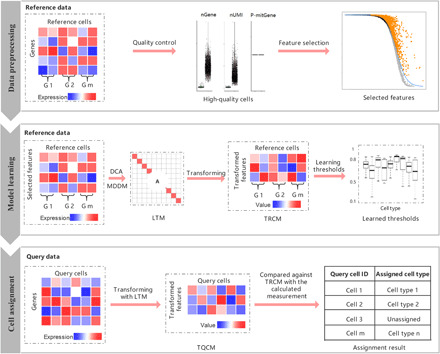
scLearn comprises three steps: data preprocessing, model learning, and cell assignment. (i) In the first step, the main processes comprise routine normalization, cell quality control, rare cell type filtering, and feature selection; nGene, number of genes; nUMI, number of unique molecular identifiers; P-mitGene, percentage of mitochondrial genes; and G, cell group. (ii) In the second step, for single-label single-cell assignment, discriminative component analysis (DCA) is applied to learn the transformation matrix. For multilabel single-cell assignment, MDDM (multilabel dimension reduction via dependence maximization) is applied to learn the transformation matrix. Then, with the learned transformation matrix, the transformed reference cell samples are obtained for the following assignment. The thresholds for labeling a cell as unassigned for each cell type are also automatically learned. LTM, learned transformation matrix, which can be calculated as the optimal transformation matrix for single-label single-cell assignment or by Eq. 6 for multilabel single-cell assignment, respectively (see Materials and Methods); TRCM, transformed reference cell matrix, which can be calculated using Eq. 1 (see Materials and Methods). (iii) In the third step, the transformed query cell samples are obtained on the basis of LTM with an available optional cell quality control procedure. The transformed query samples are compared against the TRCM to derive the measurement fulfilling the cell-type assignment with the rejection task. TQCM, transformed query cell matrix, which can be calculated using Eq. 2 (see Materials and Methods).
