Fig. 1. Aerial Observations of Manam, Papua New Guinea.
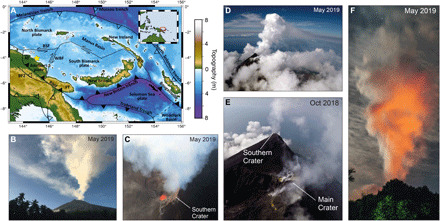
(A) Regional tectonic setting. Manam is located within the West Bismarck Volcanic Arc (yellow star). (B) The more energetic, high-altitude plume from the Southern Crater often dispersed in a different direction to the weaker, low-altitude emissions from the Main Crater. Image taken on 25 May 2019. (C) A nadir image acquired during a UAS overpass on 22 May 2019 showed that magma was present at shallow levels within the Southern Crater. A strong plume emanated from the crater. (D) View from UAS during plume approach. The buoyant plume from the Southern Crater rose to ~2 to 3 km above sea level before dispersing laterally. (E) Aerial view of the summit showing persistent passive degassing from the Southern Crater (behind the summit in this view) and the broader Main Crater area, acquired during a UAS flight on 30 October 2018 at 21:00 UTC (07:00 local time). (F) Strong nighttime incandescence reflected by the rising plume above the Southern Crater on 25 May 2019, viewed from Baliau village. Image credits: (B) E. J. Liu; (C to E) K. Wood, pilot; and (F) M. Wordell.
