Fig. 2. Targeting CDK4/6 decreased the methylation of histones mediated by SMYD2 in RCTE cells and SMYD2 also regulated the expression of CDK4 and CDK6.
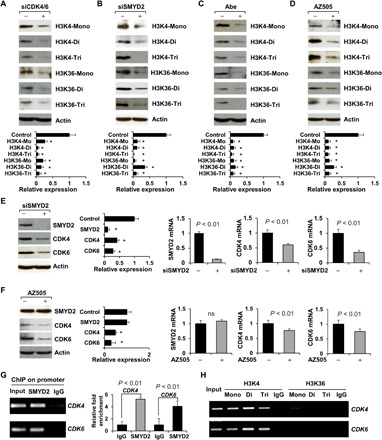
(A to D) Western blot analysis indicated that knockdown of CDK4 and CDK6 with siRNAs (A) or knockdown of SMYD2 with siRNA (B) as well as inhibition of CDK4/6 with Abe (C) or inhibition of SMYD2 with AZ505 (D) decreased the mono-, di-, and trimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 4 (H3K4) and lysine 36 (H3K36) in RCTE cells. The quantification and statistical analysis (n = 3) were shown in the graph (bottom). *P < 0.01 as compared to each control. (E and F) Knockdown (E) or inhibition (F) of SMYD2 decreased the mRNA and protein levels of CDK4 and CDK6 in RCTE cells, examined with qRT-PCR and Western blotting. *P < 0.01 as compared to each control (n = 3). ns, not significant. (G) SMYD2 bound to the promoter of CDK4 and CDK6. ChIP-qPCR analysis was performed with an SMYD2 antibody, or normal rabbit IgG in RCTE cells. (H) ChIP assay was performed with mono-, di-, and trimethylated H3K4 and H3K36 antibodies and normal rabbit IgG in RCTE cells.
