Fig. 7. Primary cilia assembly was decreased in CDK4/6 and SMYD2 up-regulated breast cancer cells and cystic renal epithelial cells, whereas targeting CDK4/6 and SMYD2 restored cilia assembly in these cells.
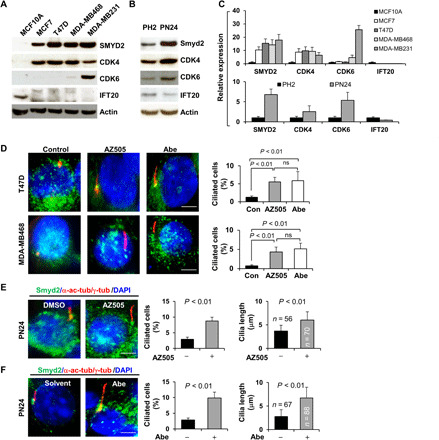
(A) Western blot of SMYD2, CDK4, CDK6, and IFT20 in normal mammary cells MCF10A and breast cancer cells, including MCF7, T47D, MDA-MB468, and MDA-MB231 cells. (B) Western blot of SMYD2, IFT20, CDK4, and CDK6 in PH2 and PN24 cells. (C) The quantification and statistical analysis (n = 3) were shown in the graphs corresponding to Fig. 6A (top) and Fig. 6B (bottom). (D to F) Representative images of T47D (top) and MDA-MB468 cells (bottom) (D) as well as PN24 cells (E and F) stained with SMYD2 (green) and α-acetyl-tubulin/γ-tubulin (red) and costained with DAPI (blue) in the presence of the SMYD2 inhibitor AZ505 (middle) and the CDK4/6 inhibitor Abe as well as vehicle. Scale bar, 5 μm. Statistical analysis of the percentage of ciliated breast cancer cells (n = 200) (P < 0.01) as well as the percentage of ciliated PN24 cells (n = 900) and their cilia lengths are shown in the graph (right). Error bars represent the SD.
